The Who, When, Why, and How of PET Amyloid Imaging in Management of Alzheimer's Disease-Review of Literature and Interesting Images
- PMID: 31242587
- PMCID: PMC6627350
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics9020065
The Who, When, Why, and How of PET Amyloid Imaging in Management of Alzheimer's Disease-Review of Literature and Interesting Images
Abstract
Amyloid imaging using positron emission tomography (PET) has an emerging role in the management of Alzheimer's disease (AD). The basis of this imaging is grounded on the fact that the hallmark of AD is the histological detection of beta amyloid plaques (Aβ) at post mortem autopsy. Currently, there are three FDA approved amyloid radiotracers used in clinical practice. This review aims to take the readers through the array of various indications for performing amyloid PET imaging in the management of AD, particularly using 18F-labelled radiopharmaceuticals. We elaborate on PET amyloid scan interpretation techniques, their limitations and potential improved specificity provided by interpretation done in tandem with genetic data such as apolipiprotein E (APO) 4 carrier status in sporadic cases and molecular information (e.g., cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) amyloid levels). We also describe the quantification methods such as the standard uptake value ratio (SUVr) method that utilizes various cutoff points for improved accuracy of diagnosing AD, such as a threshold of 1.122 (area under the curve 0.894), which has a sensitivity of 92.3% and specificity of 90.5%, whereas the cutoff points may be higher in APOE ε4 carriers (1.489) compared to non-carriers (1.313). Additionally, recommendations for future developments in this field are also provided.
Keywords: 18F-FDG; Alzheimer’s disease; PET; diagnostic imaging; molecular imaging; neurocognitive disorder; nuclear medicine; precision medicine; quantification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
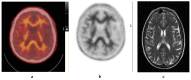
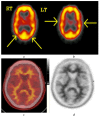

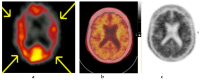
References
-
- Suppiah S., Ching S.M., Nordin A.J., Vinjamuri S. The role of PET/CT amyloid Imaging compared with Tc99m-HMPAO-SPECT imaging for diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease. Med. J. Malays. 2018;73:141–146. - PubMed
-
- Suppiah S., Andi Asri A.A., Ahmad Saad F.F., Hassan H.A., Mohtarrudin N., Chang W.L., Mahmud R., Nordin A.J. One stop centre staging by contrast-enhanced 18F-FDG PET/CT in preoperative assessment of ovarian cancer and proposed diagnostic imaging algorithm: A single centre experience in Malaysia. MJMHS. 2017;13:29–37.
-
- Ng S., Villemagne V.L., Berlangieri S., Lee S.T., Cherk M., Gong S.J., Ackermann U., Saunder T., Tochon-Danguy H., Jones G., et al. Visual Assessment Versus Quantitative Assessment of 11C-PIB PET and 18F-FDG PET for Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Nucl. Med. 2007;48:547–552. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.106.037762. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

