Approaches to CNS Drug Delivery with a Focus on Transporter-Mediated Transcytosis
- PMID: 31242683
- PMCID: PMC6627589
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20123108
Approaches to CNS Drug Delivery with a Focus on Transporter-Mediated Transcytosis
Abstract
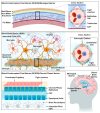
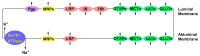
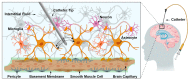
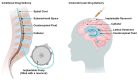
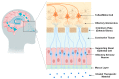
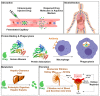
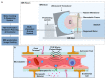
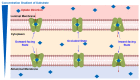
Drug delivery to the central nervous system (CNS) conferred by brain barriers is a major obstacle in the development of effective neurotherapeutics. In this review, a classification of current approaches of clinical or investigational importance for the delivery of therapeutics to the CNS is presented. This classification includes the use of formulations administered systemically that can elicit transcytosis-mediated transport by interacting with transporters expressed by transvascular endothelial cells. Neurotherapeutics can also be delivered to the CNS by means of surgical intervention using specialized catheters or implantable reservoirs. Strategies for delivering drugs to the CNS have evolved tremendously during the last two decades, yet, some factors can affect the quality of data generated in preclinical investigation, which can hamper the extension of the applications of these strategies into clinically useful tools. Here, we disclose some of these factors and propose some solutions that may prove valuable at bridging the gap between preclinical findings and clinical trials.
Keywords: Blood-brain barrier; CNS-targeted drug delivery; Efflux-pump inhibition; Receptor-mediated transcytosis; Ring-opening metathesis polymerization; Transient BBB disruption.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


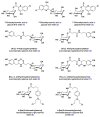
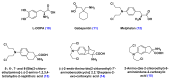



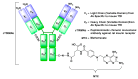

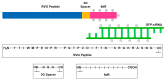

References
-
- Ruttala H.B., Ramasamy T., Poudal B.K., Choi Y., Choi J.Y., Kim J., Kwang Ku S., Choi H.G., Soon Yong C., Oh Kim J. Molecularly targeted co-delivery of a histone deacetylase inhibitor and paclitaxel by lipid-protein hybrid nanoparticles for synergistic combinational chemotherapy. Oncotarget. 2017;8:14925–14940. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14742. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Roney C., Kulkarni P., Arora V., Antich P., Bonte F., Wu A., Mallikarjuana N.N., Manohar S., Liang H.F., Kulkarni A.R., et al. Targeted nanoparticles for drug delivery through the blood–brain barrier for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Control. Release. 2005;108:193–214. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2005.07.024. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shargel L., Wu-Pong S., Yu A.B.C. Applied Biopharmaceutics & Pharmacokinetics. McGraw Hill Professional; New York, NY, USA: 2005. Drug elimination and clearance; pp. 96–116.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

