Model System for the Formation of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Replication Compartments without Viral RNA Replication
- PMID: 31243132
- PMCID: PMC6714791
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00292-19
Model System for the Formation of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Replication Compartments without Viral RNA Replication
Abstract
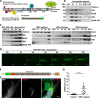
Flavivirus is a positive-sense, single-stranded RNA viral genus, with members causing severe diseases in humans such as tick-borne encephalitis, yellow fever, and dengue fever. Flaviviruses are known to cause remodeling of intracellular membranes into small cavities, where replication of the viral RNA takes place. Nonstructural (NS) proteins are not part of the virus coat and are thought to participate in the formation of these viral replication compartments (RCs). Here, we used tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) as a model for the flaviviruses and developed a stable human cell line in which the expression of NS proteins can be induced without viral RNA replication. The model system described provides a novel and benign tool for studies of the viral components under controlled expression levels. We show that the expression of six NS proteins is sufficient to induce infection-like dilation of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the formation of RC-like membrane invaginations. The NS proteins form a membrane-associated complex in the ER, and electron tomography reveals that the dilated areas of the ER are closely associated with lipid droplets and mitochondria. We propose that the NS proteins drive the remodeling of ER membranes and that viral RNA, RNA replication, viral polymerase, and TBEV structural proteins are not required.IMPORTANCE TBEV infection causes a broad spectrum of symptoms, ranging from mild fever to severe encephalitis. Similar to other flaviviruses, TBEV exploits intracellular membranes to build RCs for viral replication. The viral NS proteins have been suggested to be involved in this process; however, the mechanism of RC formation and the roles of individual NS proteins remain unclear. To study how TBEV induces membrane remodeling, we developed an inducible stable cell system expressing the TBEV NS polyprotein in the absence of viral RNA replication. Using this system, we were able to reproduce RC-like vesicles that resembled the RCs formed in flavivirus-infected cells, in terms of morphology and size. This cell system is a robust tool to facilitate studies of flavivirus RC formation and is an ideal model for the screening of antiviral agents at a lower biosafety level.
Keywords: Flaviviridae; Flp-In cell line; NS4B; flavivirus; replication compartment; replication vesicles; tick-borne encephalitis virus.
Copyright © 2019 Yau et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Compartmentalized replication organelle of flavivirus at the ER and the factors involved.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Jun;78(11):4939-4954. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03834-6. Epub 2021 Apr 12. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33846827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viperin Restricts Zika Virus and Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Replication by Targeting NS3 for Proteasomal Degradation.J Virol. 2018 Mar 14;92(7):e02054-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02054-17. Print 2018 Apr 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29321318 Free PMC article.
-
The ACBD3 protein coordinates ER-Golgi contacts to enable productive TBEV infection.J Virol. 2025 May 20;99(5):e0222424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.02224-24. Epub 2025 Apr 10. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 40207930 Free PMC article.
-
Three-dimensional architecture of tick-borne encephalitis virus replication sites and trafficking of the replicated RNA.J Virol. 2013 Jun;87(11):6469-81. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03456-12. Epub 2013 Apr 3. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23552408 Free PMC article.
-
Steps of the tick-borne encephalitis virus replication cycle that affect neuropathogenesis.Virus Res. 2005 Aug;111(2):161-74. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2005.04.007. Virus Res. 2005. PMID: 15871909 Review.
Cited by
-
Compartmentalized replication organelle of flavivirus at the ER and the factors involved.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Jun;78(11):4939-4954. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03834-6. Epub 2021 Apr 12. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33846827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flaviviruses manipulate mitochondrial processes to evade the innate immune response.Npj Viruses. 2024;2(1):47. doi: 10.1038/s44298-024-00057-x. Epub 2024 Oct 4. Npj Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39371935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recovery of a Far-Eastern Strain of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus with a Full-Length Infectious cDNA Clone.Virol Sin. 2021 Dec;36(6):1375-1386. doi: 10.1007/s12250-021-00396-6. Epub 2021 Jun 30. Virol Sin. 2021. PMID: 34191223 Free PMC article.
-
ADAM15 Participates in Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Replication.J Virol. 2021 Jan 28;95(4):e01926-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01926-20. Print 2021 Jan 28. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33208450 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of the Endogenous Lunapark Protein during Flavivirus Replication.Viruses. 2021 Jun 22;13(7):1198. doi: 10.3390/v13071198. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34206552 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

