Legionella Pneumonia Following the Heavy Rain Event of July 2018 in Japan
- PMID: 31243196
- PMCID: PMC6815902
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.2825-19
Legionella Pneumonia Following the Heavy Rain Event of July 2018 in Japan
Abstract
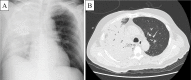
We herein report the case of a 62-year-old man diagnosed with Legionella pneumonia while engaged in recovery work in a flooded area after the Heavy Rain Event of July 2018 in Japan. The patient was intubated and maintained on mechanical ventilation and continuous hemodiafiltration. He was also administered antimicrobial therapy with ciprofloxacin and azithromycin. After 53 days in the hospital, he was discharged. It is important to recognize the risk of Legionella infection and to take measures to prevent it during recovery work that involves exposure to water and soil after a flood disaster.
Keywords: Legionella; disaster; flood; heavy rain; pneumonia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Legionnaires' disease associated with habitual drinking of hot spring water.Intern Med. 2001 Oct;40(10):1064-7. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.40.1064. Intern Med. 2001. PMID: 11688836
-
Severe Legionella pneumonia successfully treated by independent lung ventilation with intrapulmonary percussive ventilation.Respirology. 2008 May;13(3):475-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1843.2007.01220.x. Respirology. 2008. PMID: 18399877
-
Legionella pneumophila Pneumonia in Two Infants Treated with Adrenocorticotropic Hormone.J Pediatr. 2017 Jul;186:186-188.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2017.02.063. Epub 2017 Mar 20. J Pediatr. 2017. PMID: 28336145
-
[Legionnaires disease].Presse Med. 2007 Feb;36(2 Pt 2):279-87. doi: 10.1016/j.lpm.2006.10.012. Epub 2006 Dec 11. Presse Med. 2007. PMID: 17258676 Review. French.
-
[Legionella pneumonia after the use of CPAP equipment].Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2016;160:A9855. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2016. PMID: 27096478 Review. Dutch.
Cited by
-
Legionella pneumophila: The Journey from the Environment to the Blood.J Clin Med. 2022 Oct 18;11(20):6126. doi: 10.3390/jcm11206126. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36294446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Successful Treatment with Benralizumab for Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis That Developed after Disastrous Heavy Rainfall in Western Japan.Intern Med. 2021 May 1;60(9):1443-1450. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.6217-20. Epub 2020 Nov 16. Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 33191330 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary Aspergilloma and Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis Following the 2018 Heavy Rain Event in Western Japan.Intern Med. 2022 Feb 1;61(3):379-383. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.7124-21. Epub 2021 Aug 6. Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 34373373 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fire and Disaster Management Agency of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications. About the heavy rain events of July 2018 (Version 58), 2018 (in Japanese) [Internet]. [cited 2019 Jan 5]. Available from: http://www.fdma.go.jp/bn/e53c0e191d5cc01960e336b73c502b0d1f33dacd.pdf
-
- Gayer M, Connolly MA. Chapter 5: Communicable disease control after disasters. In: Public Health Consequences of Disasters. 2nd ed. Noji EK, Ed. Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2005(in revision).
-
- Stout JE, Yu VL. Legionellosis. New Engl J Med 337: 682-687, 1997. - PubMed
-
- Ebisawa K, Yamada N, Okada S, et al. . Combined Legionella and Escherichia coli lung infection after a tsunami disaster. Intern Med 50: 2233-2236, 2011. - PubMed

