HIV-associated Immune Complex Kidney Disease with C3-dominant Deposition Induced by HIV Infection after Treatment of IgA Nephropathy
- PMID: 31243235
- PMCID: PMC6859386
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.2439-18
HIV-associated Immune Complex Kidney Disease with C3-dominant Deposition Induced by HIV Infection after Treatment of IgA Nephropathy
Abstract
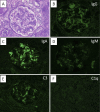
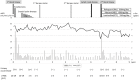
A 57-year-old man was diagnosed with IgA nephropathy. Hematuria and proteinuria were improved by tonsillectomy plus methylprednisolone pulse therapy. Lymphadenopathy, hypocomplementemia and pancytopenia were observed six years later, and urinalysis abnormalities recurred. A biopsy revealed mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis with C3-dominant deposition. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) antibody demonstrated positive conversion. He was diagnosed with HIV-associated immune complex kidney disease (HIVICK). The hematuria, proteinuria and hypocomplementemia were improved by reducing the HIV viral load through antiretroviral therapy. When C3-dominant deposition is observed on a renal biopsy, HIVICK must be differentiated.
Keywords: complement activation; human immunodeficiency virus; renal biopsy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Proliferative glomerulonephritis with monoclonal immunoglobulin G deposits complicated by immunoglobulin A nephropathy in the renal allograft.Nephrology (Carlton). 2016 Jul;21 Suppl 1:48-52. doi: 10.1111/nep.12775. Nephrology (Carlton). 2016. PMID: 26971743 Review.
-
Early tonsillectomy for severe immunoglobulin A nephropathy significantly reduces proteinuria.Pediatr Int. 2020 Sep;62(9):1054-1057. doi: 10.1111/ped.14264. Pediatr Int. 2020. PMID: 32315477
-
Immunoglobulin A Nephropathy in a Living Kidney Donor Diagnosed and Treated After Transplantation: A Case Report.Transplant Proc. 2016 Apr;48(3):940-2. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2015.10.077. Transplant Proc. 2016. PMID: 27234773
-
Clinical remission of IgA nephropathy in an HIV-positive patient after combined treatment with tonsillectomy and steroid pulse therapy.CEN Case Rep. 2015 Nov;4(2):157-161. doi: 10.1007/s13730-014-0158-6. Epub 2014 Nov 19. CEN Case Rep. 2015. PMID: 28509091 Free PMC article.
-
How to treat patients with chronic kidney disease: With special focus on IgA nephropathy.Nephrology (Carlton). 2018 Oct;23 Suppl 4:76-79. doi: 10.1111/nep.13471. Nephrology (Carlton). 2018. PMID: 30298660 Review.
Cited by
-
Secondary IgA Nephropathy and IgA-Associated Nephropathy: A Systematic Review of Case Reports.J Clin Med. 2023 Apr 6;12(7):2726. doi: 10.3390/jcm12072726. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37048809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human immunodeficiency virus-associated nephropathy mainly due to cellular variant of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis.CEN Case Rep. 2025 Jun;14(3):345-350. doi: 10.1007/s13730-025-00979-2. Epub 2025 Mar 17. CEN Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40095283 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic Aspects and Therapeutic Potential of Quercetin against COVID-19-Associated Acute Kidney Injury.Molecules. 2020 Dec 7;25(23):5772. doi: 10.3390/molecules25235772. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33297540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Catechins: Therapeutic Perspectives in COVID-19-Associated Acute Kidney Injury.Molecules. 2021 Sep 30;26(19):5951. doi: 10.3390/molecules26195951. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34641495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Immunodeficiency Virus-associated Immune Complex Kidney Disease Progressing to End-stage Kidney Disease.Intern Med. 2023 Nov 1;62(21):3183-3186. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1415-22. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Intern Med. 2023. PMID: 36927969 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weiner NJ, Goodman JW, Kimmel PL. The HIV-associated renal diseases: current insight into pathogenesis and treatment. Kidney Int 63: 1618-1631, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Nobakht E, Cohen SD, Rosenberg AZ, Kimmel PL. HIV-associated immune complex kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 12: 291-300, 2016. - PubMed
-
- Cattran DC, Coppo R, Cook HT, et al. ; Working Group of the International IgA Nephropathy Network and the Renal Pathology Society. . The Oxford classification of IgA nephropathy: rationale, clinicopathological correlations, and classification. Kidney Int 76: 534-545, 2009. - PubMed
-
- Matsuo S, Kawamura T, Joh K, et al. . Clinical guides for immunoglobulin A (IgA) nephropathy in Japan, third version. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi 53: 123-135, 2011(in Japanese). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

