Roles of circular RNAs in immune regulation and autoimmune diseases
- PMID: 31243263
- PMCID: PMC6594938
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-019-1744-5
Roles of circular RNAs in immune regulation and autoimmune diseases
Abstract
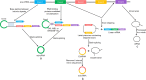
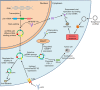
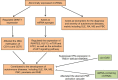
Circular RNAs (circRNAs), as a novel class of endogenously expressed non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), have a high stability and often present tissue-specific expression and evolutionary conservation. Emerging evidence has suggested that circRNAs play an essential role in complex human pathologies. Notably, circRNAs, important gene modulators in the immune system, are strongly associated with the occurrence and development of autoimmune diseases. Here, we focus on the roles of circRNAs in immune cells and immune regulation, highlighting their potential as biomarkers and biological functions in autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), multiple sclerosis (MS), primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), and psoriasis, aiming at providing new insights into the diagnosis and therapy of these diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Emerging role of long noncoding RNAs in autoimmune diseases.Autoimmun Rev. 2015 Sep;14(9):798-805. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2015.05.004. Epub 2015 May 16. Autoimmun Rev. 2015. PMID: 25989481 Review.
-
Circular RNA in autoimmune diseases: special emphasis on regulation mechanism in RA and SLE.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 12;75(3):370-384. doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgac096. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36583516
-
The critical role of epigenetics in systemic lupus erythematosus and autoimmunity.J Autoimmun. 2016 Nov;74:118-138. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2016.06.020. Epub 2016 Jul 6. J Autoimmun. 2016. PMID: 27396525 Review.
-
Implications and theragnostic potentials of circular RNAs in rheumatic diseases.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Apr 30;235:123783. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123783. Epub 2023 Feb 22. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 36822282 Review.
-
The critical importance of epigenetics in autoimmunity.J Autoimmun. 2013 Mar;41:1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2013.01.010. Epub 2013 Feb 1. J Autoimmun. 2013. PMID: 23375849 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetics in Non-tumor Immune-Mediated Skin Diseases.Mol Diagn Ther. 2021 Mar;25(2):137-161. doi: 10.1007/s40291-020-00507-1. Epub 2021 Mar 1. Mol Diagn Ther. 2021. PMID: 33646564 Review.
-
Circ_0000511 accelerates the proliferation, migration and invasion, and restrains the apoptosis of breast cancer cells through the miR‑326/TAZ axis.Int J Oncol. 2021 Apr;58(4):1. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2021.5181. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Int J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33649821 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive circRNA-microRNA-mRNA network analysis revealed the novel regulatory mechanism of Trichosporon asahii infection.Mil Med Res. 2021 Mar 9;8(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s40779-021-00311-w. Mil Med Res. 2021. PMID: 33750466 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and Bioinformatics Analysis of circRNA-miRNA-mRNA Network in Acute Myocardial Infarction.Front Genet. 2022 Mar 29;13:854993. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.854993. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35422846 Free PMC article.
-
The potential role of exosomal circRNAs in the tumor microenvironment: insights into cancer diagnosis and therapy.Theranostics. 2022 Jan 1;12(1):87-104. doi: 10.7150/thno.64096. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 34987636 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

