Integrin αvβ6 mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human bronchial epithelial cells induced by lipopolysaccharides of Pseudomonas aeruginosa via TGF-β1-Smad2/3 signaling pathway
- PMID: 31243731
- PMCID: PMC7048708
- DOI: 10.1007/s12223-019-00728-w
Integrin αvβ6 mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human bronchial epithelial cells induced by lipopolysaccharides of Pseudomonas aeruginosa via TGF-β1-Smad2/3 signaling pathway
Abstract
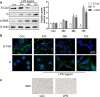
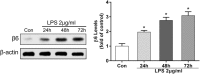
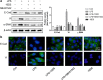
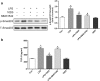
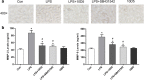
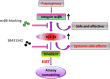
Lower respiratory tract infection due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa has become increasingly challenging, resulting in a worse morbidity and mortality. Airway remodeling is a common phenomenon in this process, to which epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) may contribute as an important promoter. Previous studies showed that epithelium-specific integrin αvβ6-mediated EMT was involved in pulmonary fibrosis via transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) signaling, but whether integrin αvβ6 plays a role in the P. aeruginosa-associated airway remodeling remains unknown. BEAS-2B cells were incubated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from P. aeruginosa in the presence or the absence of integrin αvβ6-blocking antibodies. Morphologic changes were observed by an inverted microscopy. The EMT markers were detected using Western blotting and immunofluorescence. The activation of TGF-β1-Smad2/3 signaling pathway was assessed. Furthermore, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and -9 in the medium were measured using ELISA. P. aeruginosa's LPS decreased the expression of the epithelial marker E-cadherin and promoted the mesenchymal markers, vimentin and α-smooth muscle actin in BEAS-2B cells. The expression of integrin αvβ6 was significantly increased during EMT process. Blocking integrin αvβ6 could attenuate P. aeruginosa's LPS-induced EMT markers' expression via TGF-β1-Smad2/3 signaling pathway. Furthermore, blocking integrin αvβ6 could prevent morphologic changes and oversecretion of MMP-2 and -9. Integrin αvβ6 mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human bronchial epithelial cells induced by lipopolysaccharides of P. aeruginosa via TGF-β1-Smad2/3 signaling pathway and might be a promising therapeutic target for P. aeruginosa-associated airway remodeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmed N, Pansino F, Clyde R, Murthi P, Quinn MA, Rice GE, Agrez MV, Mok S, Baker MS. Overexpression of alpha(v)beta6 integrin in serous epithelial ovarian cancer regulates extracellular matrix degradation via the plasminogen activation cascade. Carcinogenesis. 2002;23:237–244. - PubMed
-
- Almagro P, Salvado M, Garcia-Vidal C, Rodriguez-Carballeira M, Cuchi E, Torres J, Heredia JL. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and mortality after hospital admission for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respiration. 2012;84:36–43. - PubMed
-
- Botha P, Archer L, Anderson RL, Lordan J, Dark JH, Corris PA, Gould K, Fisher AJ. Pseudomonas aeruginosa colonization of the allograft after lung transplantation and the risk of bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome. Transplantation. 2008;85:771–774. - PubMed
-
- Breuss JM, Gallo J, DeLisser HM, Klimanskaya IV, Folkesson HG, Pittet JF, Nishimura SL, Aldape K, Landers DV, Carpenter W, Et A. Expression of the beta 6 integrin subunit in development, neoplasia and tissue repair suggests a role in epithelial remodeling. J Cell Sci. 1995;108:2241–2251. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

