Expression of miR-9 and miR-200c, ZEB1, ZEB2 and E-cadherin in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers in Iran
- PMID: 31244281
- PMCID: PMC7021597
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.6.1633
Expression of miR-9 and miR-200c, ZEB1, ZEB2 and E-cadherin in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers in Iran
Abstract
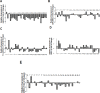
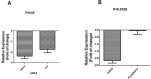
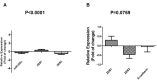
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) exert a critical influence on physiological and pathological processes through posttranscriptional modification of their mRNA targets. They play important roles in tumorigenesis and are considered to be potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers with various cancers. MiR-200c and miR-9 are regulatory elements that can have dual impacts as oncogenes and/or tumor suppressor genes. MiR-200c regulates two transcription factors, ZEB1 and ZEB2, while miR-9 is a regulatory factor for the E-cadherin protein which has a critical function in cell-cell junctions and is inhibited by two transcription factors ZEB1 and ZEB2. In this study, expression levels of miR-200c and miR-9, ZEB-1, ZEB-2 and E-cadherin were assessed in 30 non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) by real-time qPCR. MiR-9 was down-regulated significantly in tumor tissues compared to normal adjacent tissues, while there was no significant change in expression level of miR-200c. On the other hand, ZEB1 demonstrated significant increase and ZEB2a decrease at the mRNA level. These results indicate roles for miR-9 and ZEB1 in genesis of lung cancer, although clinico-pathological associations were not evident. Further studies are necessary to assess implications for treatment of lung cancer.
Keywords: MicroRNAs; miR-200c; miR-9; non-small cell lung cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression level of microRNA-200c is associated with cell morphology in vitro and histological differentiation through regulation of ZEB1/2 and E-cadherin in gastric carcinoma.Oncol Rep. 2018 Jan;39(1):91-100. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.6093. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29138864 Free PMC article.
-
miR-200c: a versatile watchdog in cancer progression, EMT, and drug resistance.J Mol Med (Berl). 2016 Jun;94(6):629-44. doi: 10.1007/s00109-016-1420-5. Epub 2016 Apr 20. J Mol Med (Berl). 2016. PMID: 27094812 Review.
-
Role of miR-200c/miR-141 in the regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and migration in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Int J Mol Med. 2014 Apr;33(4):879-86. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.1625. Epub 2014 Jan 14. Int J Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24424572
-
MicroRNA-200c regulates cisplatin resistance by targeting ZEB2 in human gastric cancer cells.Oncol Rep. 2017 Jul;38(1):151-158. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5659. Epub 2017 May 22. Oncol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28534959
-
Role of ZEB Family Members in Proliferation, Metastasis, and Chemoresistance of Prostate Cancer Cells: Revealing Signaling Networks.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2021;21(9):749-767. doi: 10.2174/1568009621666210601114631. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2021. PMID: 34077345 Review.
Cited by
-
Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition Signaling Pathways Responsible for Breast Cancer Metastasis.Cell Mol Bioeng. 2021 Sep 2;15(1):1-13. doi: 10.1007/s12195-021-00694-9. eCollection 2022 Feb. Cell Mol Bioeng. 2021. PMID: 35096183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zeb2 DNA-Binding Sites in Neuroprogenitor Cells Reveal Autoregulation and Affirm Neurodevelopmental Defects, Including in Mowat-Wilson Syndrome.Genes (Basel). 2023 Mar 2;14(3):629. doi: 10.3390/genes14030629. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36980900 Free PMC article.
-
miR-9-5p facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting ESR1.Mol Cell Biochem. 2021 Feb;476(2):575-583. doi: 10.1007/s11010-020-03927-z. Epub 2020 Oct 27. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33106914
-
Use of recombinant microRNAs as antimetabolites to inhibit human non-small cell lung cancer.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023 Oct;13(10):4273-4290. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.011. Epub 2023 Jul 15. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023. PMID: 37799388 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of MicroRNAs in the Pathogenesis of Doxorubicin-Induced Vascular Remodeling.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 12;25(24):13335. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413335. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769102 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen J, Wang W, Zhang Y, Hu T, Chen Y. The roles of miR-200c in colon cancer and associated molecular mechanisms. Tumor Biol. 2014;35:6475–83. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

