Impact of heat processing on the nutritional content of Gryllus bimaculatus (black cricket)
- PMID: 31244552
- PMCID: PMC6582549
- DOI: 10.1111/nbu.12374
Impact of heat processing on the nutritional content of Gryllus bimaculatus (black cricket)
Abstract
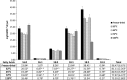
Insects are increasingly suggested as a potential novel solution to global nutrition challenges. However, limited research is available on the impact of processing methods on the nutritional content of edible insects. This trial examines the effect of heat processing on the nutritional profile of the black cricket, Gryllus bimaculatus. Adult black crickets were killed by freezing and then dried at either a low (45°C) or high (120°C) temperature followed by nutritional analysis of protein and micronutrient content. An additional set of samples was either freeze-dried or dried at 32, 45, 72 or 120°C followed by nutritional analysis of lipid content. Analysis showed that percentage protein content was significantly higher in crickets dried at 45°C, a difference of roughly 1% of the total weight. Similarly, calcium content was also significantly higher in crickets dried at 45°C, although no other measured micronutrients were affected. Additionally, the fatty acid content was significantly influenced by higher temperature processing. Freeze-drying black crickets conserved significantly more of the long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids than drying at 120°C. Insects hold potential as a source of essential nutrients and fatty acids; however, consideration must be given to heat processing at high temperatures as this may affect the nutritional profile.
Keywords: black crickets; edible insects; heat processing; nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors certify that they have no affiliations with, or involvement in, any organisation or entity with any financial interest or non‐financial interest in the subject matter or matters discussed in this manuscript.
Figures


References
-
- Aaes‐Jørgensen E (1977) Certain aspects of polyunsaturated fatty acids in nutrition. Bibliotheca nutritio et dieta 25: 17‐23. - PubMed
-
- Adeboye AO, Bolaji TA & Fatola OL (2016) Nutritional composition and sensory evaluation of cookies made from wheat and palm weevil larvae flour blends. Annals of Food Science and Technology 17: 543–7.
-
- Aniebo AO & Owen OJ (2010) Effects of age and method of drying on the proximate composition of housefly larvae (Musca domestica Linnaeus) meal (HFLM). Pakistan Journal of Nutrition 9: 485–7.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

