Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells: A Race to Revolutionize Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 31244578
- PMCID: PMC6558337
- DOI: 10.1159/000496870
Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells: A Race to Revolutionize Cancer Therapy
Abstract
For years, cancer treatment was dominated by chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and stem cell transplantation. New insights into genetic characteristics of leukemic cells have initiated the development of the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy. This type of adoptive cell immunotherapy has been a breakthrough in the treatment of aggressive B-cell lymphoma and B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. In August 2018, the European Commission has approved the first CAR T-cell products - tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah®, Novartis) and axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta®, Gilead) - for hematological neoplasms in Europe. As CAR T cells are a living drug, its benefits can last for many years. The administration of CAR T cells is a complex and costly endeavor involving cell manufacture, shipping of apheresis products, and management of novel and severe adverse reactions. The most common toxicities observed after CAR T-cell therapy are cytokine release syndrome and immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome. Current research focuses on improved safety and efficacy in hematological malignancies as well as the translation of CAR T-cell therapy to solid tumors. This review covers the development and current status of CAR T-cell therapy in a clinical setting with focus on challenges and future opportunities.
Keywords: Cancer immunotherapy; Chimeric antigen receptor T cells; Lymphoma; Toxicities.
Figures
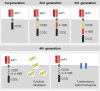
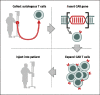
References
-
- Kolb HJ. Donor leukocyte transfusions for treatment of leukemic relapse after bone marrow transplantation. EBMT Immunology and Chronic Leukemia Working Parties. Vox Sang. 1998;74((2 Suppl 2)):321–9. - PubMed
-
- European Medicines Agency [Internet] Blincyto (blinatumomab) Assessment history [cited 2018 Sep 05]. Available from: http://www.ema.europa.eu/ema/index.jsp?curl=pages/medicines/human/medici....
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

