A Novel Transwell Blood Brain Barrier Model Using Primary Human Cells
- PMID: 31244605
- PMCID: PMC6563620
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00230
A Novel Transwell Blood Brain Barrier Model Using Primary Human Cells
Abstract
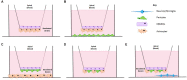
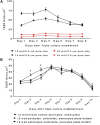
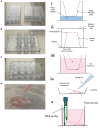
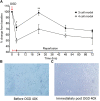
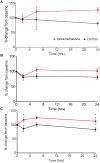
Structural alterations and breakdown of the blood brain barrier (BBB) is often a primary or secondary consequence of disease, resulting in brain oedema and the transport of unwanted substances into the brain. It is critical that effective in vitro models are developed to model the in vivo environment to aid in clinically relevant research, especially regarding drug screening and permeability studies. Our novel model uses only primary human cells and includes four of the key cells of the BBB: astrocytes, pericytes, brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMEC) and neurons. We show that using a larger membrane pore size (3.0 μM) there is an improved connection between the endothelial cells, astrocytes and pericytes. Compared to a two and three cell model, we show that when neurons are added to HBMECs, astrocytes and pericytes, BBB integrity was more sensitive to oxygen-glucose deprivation evidenced by increased permeability and markers of cell damage. Our data also show that a four cell model responds faster to the barrier tightening effects of glucocorticoid dexamethasone, when compared to a two cell and three cell model. These data highlight the important role that neurons play in response to ischaemia, particularly how they contribute to BBB maintenance and breakdown. We consider that this model is more representative of the interactions at the neurovascular unit than other transwell models and is a useful method to study BBB physiology.
Keywords: BBB model; BBB permeability; blood-brain barrier; in vitro; primary human cells; stroke; transwell.
Figures
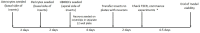
References
-
- Appelt-Menzel A., Cubukova A., Günther K., Edenhofer F., Piontek J., Krause G., et al. (2017). Establishment of a human blood-brain barrier co-culture model mimicking the neurovascular unit using induced pluri- and multipotent stem cells. Stem Cell Rep. 8 894–906. 10.1016/j.stemcr.2017.02.021 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

