Systematic Overview of Aristolochic Acids: Nephrotoxicity, Carcinogenicity, and Underlying Mechanisms
- PMID: 31244661
- PMCID: PMC6580798
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00648
Systematic Overview of Aristolochic Acids: Nephrotoxicity, Carcinogenicity, and Underlying Mechanisms
Abstract
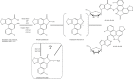
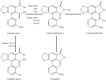
Aristolochic acids (AAs) are a group of toxins commonly present in the plants of genus Aristolochia and Asarum, which are spread all over the world. Since the 1990s, AA-induced nephropathy (AAN) and upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC) have been reported in many countries. The underlying mechanisms of AAN and AA-induced UTUC have been extensively investigated. AA-derived DNA adducts are recognized as specific biomarkers of AA exposure, and a mutational signature predominantly characterized by A→T transversions has been detected in AA-induced UTUC tumor tissues. In addition, various enzymes and organic anion transporters are involved in AA-induced adverse reactions. The progressive lesions and mutational events initiated by AAs are irreversible, and no effective therapeutic regimen for AAN and AA-induced UTUC has been established until now. Because of several warnings on the toxic effects of AAs by the US Food and Drug Administration and the regulatory authorities of some other countries, the sale and use of AA-containing products have been banned or restricted in most countries. However, AA-related adverse events still occur, especially in the Asian and Balkan regions. Therefore, the use of AA-containing herbal remedies and the consumption of food contaminated by AAs still carry high risk. More strict precautions should be taken to protect the public from AA exposure.
Keywords: Balkan endemic nephropathy; aristolochic acid nephropathy; aristolochic acids; carcinogenicity of aristolochic acids; mechanisms of nephrotoxicity; upper tract urothelial carcinoma.
Figures
References
-
- Abdullah R., Diaz L. N., Wesseling S., Rietjens I. M. (2017). Risk assessment of plant food supplements and other herbal products containing aristolochic acids using the margin of exposure (MOE) approach. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 34 (2), 135–144. 10.1080/19440049.2016.1266098 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ardalan M. R., Khodaie L., Nasri H., Jouyban A. (2015). Herbs and hazards: risk of aristolochic acid nephropathy in Iran. Iran J. Kidney Dis. 9 (1), 14–17. http//dx..org/ - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources