The Effect of Mindfulness Interventions for Parents on Parenting Stress and Youth Psychological Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 31244732
- PMCID: PMC6562566
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01336
The Effect of Mindfulness Interventions for Parents on Parenting Stress and Youth Psychological Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: The psychological well-being of parents and children is compromised in families characterized by greater parenting stress. As parental mindfulness is associated with lower parenting stress, a growing number of studies have investigated whether mindfulness interventions can improve outcomes for families. This systematic review and meta-analysis evaluates the effectiveness of mindfulness interventions for parents, in reducing parenting stress and improving youth psychological outcomes. Methods: A literature search for peer-reviewed articles and dissertations was conducted in accordance with PRISMA guidelines in the PsycInfo, Medline, PubMed, CINAHL, Web of Science, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, and ProQuest Dissertations & Theses databases. Studies were included if they reported on a mindfulness-based intervention delivered in person to parents with the primary aim of reducing parenting stress or improving youth psychological outcomes. Results: Twenty-five independent studies were included in the review. Eighteen studies used a single group design and six were randomized controlled trials. Within-groups, meta-analysis indicated a small, post-intervention reduction in parenting stress (g = 0.34), growing to a moderate reduction at 2 month follow-up (g = 0.53). Overall, there was a small improvement in youth outcomes (g = 0.27). Neither youth age or clinical status, nor time in mindfulness training, moderated parenting stress or overall youth outcome effects. Youth outcomes were not moderated by intervention group attendees. Change in parenting stress predicted change in youth externalizing and cognitive effects, but not internalizing effects. In controlled studies, parenting stress reduced more in mindfulness groups than control groups (g = 0.44). Overall, risk of bias was assessed as serious. Conclusions: Mindfulness interventions for parents may reduce parenting stress and improve youth psychological functioning. While improvements in youth externalizing and cognitive outcomes may be explained by reductions in parenting stress, it appears that other parenting factors may contribute to improvements in youth internalizing outcomes. Methodological weaknesses in the reviewed literature prevent firm conclusions from being drawn regarding effectiveness. Future research should address these methodological issues before mindfulness interventions for parents are recommended as an effective treatment option for parents or their children.
Keywords: child externalizing; child internalizing; meta-analysis; mindful parenting; mindfulness; parenting intervention; parenting stress; systematic review.
Figures



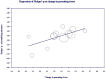

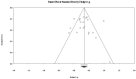

Similar articles
-
The effectiveness of mindful parenting programs in promoting parents' and children's wellbeing: a systematic review.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Mar;14(3):139-80. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-2314. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27532143
-
Mindfulness for children with ADHD and Mindful Parenting (MindChamp): Protocol of a randomised controlled trial comparing a family Mindfulness-Based Intervention as an add-on to care-as-usual with care-as-usual only.BMC Psychiatry. 2018 Jul 25;18(1):237. doi: 10.1186/s12888-018-1811-y. BMC Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 30045714 Free PMC article.
-
Stress management interventions among socioeconomically disadvantaged parents: A meta-analysis and moderation analysis.Int J Nurs Stud. 2021 Aug;120:103954. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2021.103954. Epub 2021 Apr 24. Int J Nurs Stud. 2021. PMID: 34111700 Review.
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
Mindful Parenting Group Intervention for Parents of Children with Anxiety Disorders.Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2024 Oct;55(5):1342-1353. doi: 10.1007/s10578-023-01492-2. Epub 2023 Jan 23. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2024. PMID: 36689038 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The effects of mindfulness upbringing perception on social entrepreneurship orientation: A moderated mediation model of prosocial motivation and perceived pressure from external stakeholders.Front Psychol. 2022 Oct 13;13:968484. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.968484. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 36312148 Free PMC article.
-
The Father's Part: A Pilot Evaluation of a Father-Centered Family Intervention Group in Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.Behav Sci (Basel). 2023 Dec 22;14(1):13. doi: 10.3390/bs14010013. Behav Sci (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38247664 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-Directed Care: Why Neuroscience Principles Direct PICU Management beyond the ABCs.Children (Basel). 2022 Dec 9;9(12):1938. doi: 10.3390/children9121938. Children (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36553381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using Photovoice in a Mindfulness-Based Program to Understand the Experiences of Caregivers of Young Adults with Psychosis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Nov 22;19(23):15461. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192315461. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36497535 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Parental stress in families of children with special educational needs: a systematic review.Front Psychiatry. 2023 Aug 10;14:1198302. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1198302. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37636816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abidin R. R. (1983). Parenting Stress Index manual. Charlottesville: Pediatric Psychology Press.
-
- Abidin R. R. (1995). Parenting Stress Index: Professional Manual 3rd ed Odessa, FL: Psychological Assessment Resources Inc.
-
- Achenbach T. M. (1991a). Manual for the Youth Self-Report and 1991 Profile. Burlington: University of Vermont.
-
- Achenbach T. M. (1991b). Manual for the Child Behaviour Checklist/4-18 and 1991 Profile. Burlington: University of Vermont.
-
- Anthony L. G., Anthony B. J., Glanville D. N., Naiman D. Q., Waanders C., Shaffer S. (2005). The relationships between parenting stress, parenting behaviour and preschoolers' social competence and behaviour problems in the classroom. Infant Child Dev. 14, 133–154. 10.1002/icd.385 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

