Non-canonical Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in Cancer: Activation of GLI Transcription Factors Beyond Smoothened
- PMID: 31244888
- PMCID: PMC6581679
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00556
Non-canonical Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in Cancer: Activation of GLI Transcription Factors Beyond Smoothened
Abstract
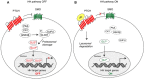
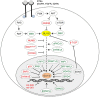
The Hedgehog-GLI (HH-GLI) pathway is a highly conserved signaling that plays a critical role in controlling cell specification, cell-cell interaction and tissue patterning during embryonic development. Canonical activation of HH-GLI signaling occurs through binding of HH ligands to the twelve-pass transmembrane receptor Patched 1 (PTCH1), which derepresses the seven-pass transmembrane G protein-coupled receptor Smoothened (SMO). Thus, active SMO initiates a complex intracellular cascade that leads to the activation of the three GLI transcription factors, the final effectors of the HH-GLI pathway. Aberrant activation of this signaling has been implicated in a wide variety of tumors, such as those of the brain, skin, breast, gastrointestinal, lung, pancreas, prostate and ovary. In several of these cases, activation of HH-GLI signaling is mediated by overproduction of HH ligands (e.g., prostate cancer), loss-of-function mutations in PTCH1 or gain-of-function mutations in SMO, which occur in the majority of basal cell carcinoma (BCC), SHH-subtype medulloblastoma and rhabdomyosarcoma. Besides the classical canonical ligand-PTCH1-SMO route, mounting evidence points toward additional, non-canonical ways of GLI activation in cancer. By non-canonical we refer to all those mechanisms of activation of the GLI transcription factors occurring independently of SMO. Often, in a given cancer type canonical and non-canonical activation of HH-GLI signaling co-exist, and in some cancer types, more than one mechanism of non-canonical activation may occur. Tumors harboring non-canonical HH-GLI signaling are less sensitive to SMO inhibition, posing a threat for therapeutic efficacy of these antagonists. Here we will review the most recent findings on the involvement of alternative signaling pathways in inducing GLI activity in cancer and stem cells. We will also discuss the rationale of targeting these oncogenic pathways in combination with HH-GLI inhibitors as a promising anti-cancer therapies.
Keywords: GLI; Hedgehog; cancer; non-canonical; oncogene; targeted therapy; tumor suppressor.
Figures

Comment in
-
Combined targeting of HEDGEHOG signaling and BRD4 as a novel therapeutic option against melanoma.Oncotarget. 2023 May 26;14:526-527. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28441. Oncotarget. 2023. PMID: 37235835 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

