Factors Determining the Success of Therapeutic Lifestyle Interventions in Diabetes - Role of Partner and Family Support
- PMID: 31244906
- PMCID: PMC6587903
- DOI: 10.17925/EE.2019.15.1.18
Factors Determining the Success of Therapeutic Lifestyle Interventions in Diabetes - Role of Partner and Family Support
Abstract
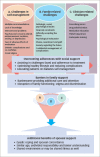
Background and aims: Knowledge of therapeutic lifestyle interventions is one of the most important pillars of diabetes care; however, its incorporation in real-world settings is poor. This review evaluates the role of partner and family support in diabetes management. Methods: Literature searches were performed in PubMed, Medline and Embase for articles published before July 2018, using the terms "therapeutic lifestyle intervention" [MeSH Terms], OR "diet changes" [All Fields], OR "spousal participation" [All Fields], OR "lifestyle interventions" [All Fields], "lifestyle changes" [All Fields] AND "diabetes" [All Fields]. The search was not restricted to English-language literature; literature in Spanish, French and German were also evaluated. Results: A total of 66 of articles were reviewed, which included 33 original work, 21 review articles, and 12 systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Studies and meta-analyses have showed that if one partner has type-2 diabetes this increases the risk in other by 5-26%. Partner and family have similar diet, lifestyle, and micro- and macro-environments which could explain the similar increased risk of diabetes and non-communicable diseases. Studies have consistently shown that spousal and family support plays a key role in overcoming negative behaviours and optimising behaviours in diabetes control. Partner support has major role in prevention and control of diabetes distress, associated depression, and medication non-compliance which have an adverse impact in glycaemic outcomes. These data are predominantly available from observational studies. There is paucity of data from interventional trials evaluating effects of family and spousal participation on health, glycaemic control and quality of life. Conclusion: The support of family and spouse/partner is beneficial to improve adherence to the lifestyle interventions and pharmacotherapy required to achieve optimum glycaemic control and avoid associated complications.
Keywords: Diabetes; challenges; lifestyle management; partner participation; relationships.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: Lovely Gupta, Deepak Khandelwal, Priti Rishi Lal, Yasheep Gupta, Sanjay Kalra and Deep Dutta have no conflicts of interest to declare in relation to this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Promoting and supporting self-management for adults living in the community with physical chronic illness: A systematic review of the effectiveness and meaningfulness of the patient-practitioner encounter.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009;7(13):492-582. doi: 10.11124/01938924-200907130-00001. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009. PMID: 27819974
-
The Effectiveness of Integrated Care Pathways for Adults and Children in Health Care Settings: A Systematic Review.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009;7(3):80-129. doi: 10.11124/01938924-200907030-00001. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009. PMID: 27820426
-
The effect of weight management interventions that include a diet component on weight-related outcomes in pregnant and postpartum women: a systematic review protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Jan;13(1):88-98. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-1812. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26447010
-
Factors associated with glycaemic control in patients with diabetes mellitus: A systematic literature review.J Clin Nurs. 2019 May;28(9-10):1433-1450. doi: 10.1111/jocn.14795. Epub 2019 Feb 12. J Clin Nurs. 2019. PMID: 30667583
-
Lifestyle interventions for type 2 diabetes prevention in women with prior gestational diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of behavioural, anthropometric and metabolic outcomes.Prev Med Rep. 2015 May 24;2:448-61. doi: 10.1016/j.pmedr.2015.05.009. eCollection 2015. Prev Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 26844102 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Community Health Volunteer Involvement Program for Glycated Hemoglobin Reduction Among Thai Patients With Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes: A Mixed-Method Study.J Prim Care Community Health. 2022 Jan-Dec;13:21501319221077960. doi: 10.1177/21501319221077960. J Prim Care Community Health. 2022. PMID: 35184585 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical traits and systemic risks of familial diabetes mellitus according to age of onset and quantity: an analysis of data from the community-based KoGES cohort study.Epidemiol Health. 2023;45:e2023029. doi: 10.4178/epih.e2023029. Epub 2023 Feb 23. Epidemiol Health. 2023. PMID: 36915273 Free PMC article.
-
Process evaluation protocol of a cluster randomised trial for a scalable solution for delivery of Diabetes Self-Management Education in Thailand (DSME-T).BMJ Open. 2021 Dec 9;11(12):e056141. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-056141. BMJ Open. 2021. PMID: 34887283 Free PMC article.
-
The Outlook of Healthcare Providers on the Involvement of Diabetic Patients as Health Promoters for Diabetes Prevention Among Their Family Members: A Qualitative Study.Cureus. 2023 Jul 19;15(7):e42108. doi: 10.7759/cureus.42108. eCollection 2023 Jul. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37602072 Free PMC article.
-
Spousal Involvement in Collaborative Management and Glycemic Behavior Change among Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review.SAGE Open Nurs. 2024 Apr 18;10:23779608241245196. doi: 10.1177/23779608241245196. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. SAGE Open Nurs. 2024. PMID: 38638412 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- IDF Diabetes Atlas –. 8th Edition. 2017. www.diabetesatlas.org/resources/2017-atlas.html Available at: (accessed 24 August 2018)
-
- Dutta D, Mukhopadhyay S. et al. Incidence of diabetes and prediabetes and predictors of progression among Asian Indians: 10-year follow-up of the chennai urban rural epidemiology study (CURES). Diabetes Care. Diabetes Care. 2015;2015 Sep;3838((9)):1441–1448.. doi: 10.2337/dc15-0908. Comment on Anjana. e146. [Epub ahead of print]. - DOI - PubMed
-
- NDTV, World Diabetes Day 2017: Number of Diabetics to Double In India by 2023, 2017. www.ndtv.com/food/world-diabetes-day-2017-number-of-diabetics-to-double-... Available at: (accessed 24 August 2018).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources