Supramolecular nanotheranostics based on pillarenes
- PMID: 31244942
- PMCID: PMC6567958
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.31858
Supramolecular nanotheranostics based on pillarenes
Abstract
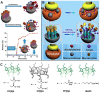
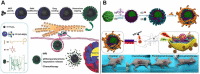
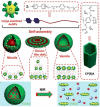
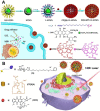
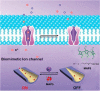
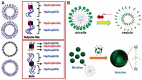
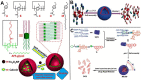
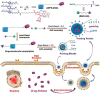
With the rapid development of supramolecular chemistry and nanomaterials, supramolecular nanotheranostics has attracted remarkable attention owing to the advantages compared with conventional medicine. Supramolecular architectures relying on non-covalent interactions possess reversible and stimuli-responsive features; endowing supramolecular nanotheranostics based on supramolecular assemblies great potentials for the fabrication of integrated novel nanomedicines and controlled drug delivery systems. In particular, pillarenes, as a relatively new class of synthetic macrocycles, are important candidates in the construction of supramolecular therapeutic systems due to their excellent features such as rigid and symmetric structures, facile substitution, and unique host-guest properties. This review summarizes the development of pillarene-based supramolecular nanotheranostics for applications in biological mimicking, virus inhibition, cancer therapy, and diagnosis, which contains the following two major parts: (a) pillarene-based hybrid supramolecular nanotheranostics upon hybridizing with porous materials such as mesoporous silica nanoparticles, metal-organic frameworks, metal nanoparticles, and other inorganic materials; (b) pillarene-based organic supramolecular therapeutic systems that include supramolecular amphiphilic systems, artificial channels, and prodrugs based on host-guest complexes. Finally, perspectives on how pillarene-based supramolecular nanotheranostics will advance the field of pharmaceuticals and therapeutics are given.
Keywords: Drug delivery; hybrid materials; macrocyclic arenes; nanotheranostics; supramolecular chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures






References
-
- Gravel J, Schmitzer AR. Imidazolium and benzimidazolium-containing compounds: from simple toxic salts to highly bioactive drugs. Org Biomol Chem. 2017;15:1051–71. - PubMed
-
- Song N, Yang Y-W. Molecular and supramolecular switches on mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chem Soc Rev. 2015;44:3474–504. - PubMed
-
- Wen J, Yang K, Liu F, Li H, Xu Y, Sun S. Diverse gatekeepers for mesoporous silica nanoparticle based drug delivery systems. Chem Soc Rev. 2017;46:6024–45. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen KT, Zhao Y. Engineered hybrid nanoparticles for on-demand diagnostics and therapeutics. Acc Chem Res. 2015;48:3016–25. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

