Multimodality imaging in carcinoid heart disease
- PMID: 31245014
- PMCID: PMC6560671
- DOI: 10.1136/openhrt-2019-001060
Multimodality imaging in carcinoid heart disease
Abstract
Neuroendocrine neoplasms arise from the gastrointestinal tract and can lead to carcinoid syndrome. Carcinoid heart disease affects more than half of these patients and is the initial presentation of carcinoid syndrome in up to 20 % of patients. Carcinoid heart disease typically leads to valve dysfunction, but in rare instances, carcinoid tumours can also metastasise to the endocardium and myocardium. Cardiovascular imaging plays an integral role in the diagnosis and prognosis of carcinoid heart disease. The use of multimodality imaging techniques including echocardiography, cardiac MRI, cardiovascular CT and positron emission tomography have allowed for a more comprehensive assessment of carcinoid heart disease. In this review, we discuss the features of carcinoid heart disease observed on multimodality imaging, indications for obtaining imaging studies and their role in carcinoid heart disease management.
Keywords: cardiac remodelling; echocardiography; tricuspid valve disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
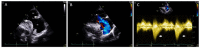
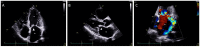
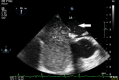
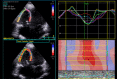
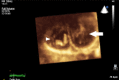
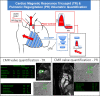
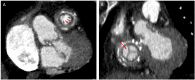
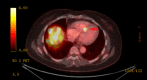

References
-
- Habib G, Bucciarelli-Ducci C, Caforio ALP, et al. . Multimodality Imaging in Restrictive Cardiomyopathies: An EACVI expert consensus document In collaboration with the "Working Group on myocardial and pericardial diseases" of the European Society of Cardiology Endorsed by The Indian Academy of Echocardiography. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 2017;18:1090–121. 10.1093/ehjci/jex034 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
