Hoffa's Fat Pad-associated Solitary Neurofibroma as the Cause of Anterior Knee Pain: A Case Report
- PMID: 31245314
- PMCID: PMC6588136
- DOI: 10.13107/jocr.2250-0685.1294
Hoffa's Fat Pad-associated Solitary Neurofibroma as the Cause of Anterior Knee Pain: A Case Report
Abstract
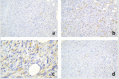
Introduction: Infrapatellar peripheral neural tumors, particularly neurofibromas, are rather rare entities reported in the literature. They are slow-growing lesions that usually do not exhibit clinical manifestations other than interspecific swelling or pain; hence, their diagnosis can be quite challenging. Therefore, scrutiny should include not only traditional clinical assessment and imaging but also more specific molecular biology techniques, such as immunohistochemistry.
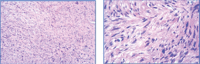
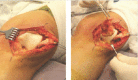
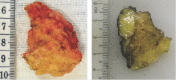
Case report: We present the clinical, imaging, histological, and immunohistochemical features of a unique case of solitary neurofibromain a 33-year-old female presenting chronic anterior knee pain. The tumor was completely removed through a surgical approach.
Conclusions: Although cases of a solitary neurofibroma originating within Hoffa's fat pad are extremely rare; the entity should be considered in the differential diagnosis when symptomatology is not alleviated with appropriate treatments.
Keywords: Anterior knee pain; Hoffa’s fat pad; immunohistochemistry; solitary neurofibroma.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: Nil
Figures

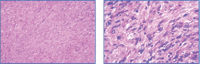
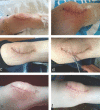
References
-
- Pradilla-Gordillo MP. Solitary neurofibroma in cervical nerve root C7. Rev Iberoam Cir Mano. 2016;44:35–8.
-
- Argenyi ZB. Neural and neuroendocrine neoplasm (other than neurofibromatosis) In: Bolognia J, Jorizzo J, Rapini R, editors. Dermatology. 2nd ed. Madrid: Mosby; 2008. pp. 1795–811.
-
- Reyes-Martínez G, Plascencia-Gómez JA, de Anda-Juárez MC, Gómez-Villa R, Sáenz-Corral C, Carreón AA, et al. Solitary neurofibroma:Its frequency in a general hospital in Mexico City. Dermatol CQM. 2012;10:8–12.
-
- McDonald JS. Tumors of the oral soft tissues and cysts and tumors of the bones. In: Dean JA, editor. McDonald and Avery's Dentistry for the Child and Adolescent. 10th ed. USA: Elsevier; 2016. pp. 603–26.
-
- Zheng H, Chang L, Patel N, Yang J, Lowe L, Burns DK, et al. Induction of abnormal proliferation by nonmyelinating Schwann cells triggers neurofibroma formation. Cancer Cell. 2008;13:117–28. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
