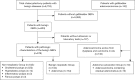
Neoplastic polyps in gallbladder: a retrospective study to determine risk factors and treatment strategy for gallbladder polyps
- PMID: 31245402
- PMCID: PMC6561872
- DOI: 10.21037/hbsn.2018.12.15
Neoplastic polyps in gallbladder: a retrospective study to determine risk factors and treatment strategy for gallbladder polyps
Abstract
Background: Preoperative differentiation of malignant and premalignant gallbladder polyps (GBPs) from benign lesions is a key imperative to guide treatment decision-making. We aimed to characterize the various types of GBPs and sought to identify the risk factors for neoplastic polyps. Our findings may help optimize treatment strategy.
Methods: Retrospective analysis of 686 patients with post-cholecystectomy pathologically-proven GBPs between January 2003 and December 2016. The patients were classified into non-neoplastic polyp group, benign neoplastic polyp group, and adenoma canceration group. Clinical features, ultrasound findings, and results of laboratory investigations and histopathological examination were reviewed and compared between the groups.
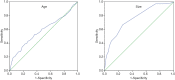
Results: Out of 686 patients, 542 (79.0%) had non-neoplastic polyps, 134 (19.5%) had neoplastic polyps, and 10 (1.5%) had adenoma canceration. The mean age was 46.06±12.12 years; 383 (55.8%) patients were female. The median (25th percentile, 75th percentile) time between diagnosis and surgery in the cholesterol polyp group [24 (3.5, 60) months] was significantly longer than that in adenoma [12 (2, 60) months] and adenoma canceration [5 (0.475, 12) months] groups. The mean diameter was 1.14±0.61 cm (range, 0.5-8.4 cm). Three hundred twelve (45.5%) patients had solitary polyps and intralesional blood flow was observed in 41 (6.0%) patients. On univariate analysis, age >49.5 years, polyp size >1.15 cm, solitary polyp, intralesional blood flow, absence of symptoms, and lack of cholecystitis showed a significant association with adenoma. On multivariate analysis, polyp size (>1.15 cm), intralesional blood flow, and lack of cholecystitis were independent predictors of adenoma.
Conclusions: Polyp size >1.15 cm, intralesional blood flow, and lack of cholecystitis were predictors of neoplastic polyps. Malignant transformation of adenoma may occur over a relatively short time.
Keywords: Gallbladder polyp (GBP); adenoma; cholesterol; malignancy; predictive factors.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Surgical treatment of polypoid lesions of gallbladder].Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2003 Jul-Aug;131(7-8):319-24. doi: 10.2298/sarh0308319p. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2003. PMID: 14692147 Serbian.
-
Predictive factors of neoplastic gallbladder polyps: Outcomes of 278 patients.Turk J Gastroenterol. 2017 May;28(3):202-206. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2017.16698. Epub 2017 Mar 17. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28316322
-
Polyp size of 1 cm is insufficient to discriminate neoplastic and non-neoplastic gallbladder polyps.Surg Endosc. 2019 May;33(5):1564-1571. doi: 10.1007/s00464-018-6444-1. Epub 2018 Sep 10. Surg Endosc. 2019. PMID: 30203209 Free PMC article.
-
Malignant transformation of a 5-mm gallbladder polyp over 2 years: a case report and review of current literature.Ultrasound Q. 2015 Mar;31(1):66-8. doi: 10.1097/RUQ.0000000000000094. Ultrasound Q. 2015. PMID: 25054905 Review.
-
Diagnosis and Treatment of Gallbladder Polyps: Current Perspectives.Euroasian J Hepatogastroenterol. 2019 Jan-Jun;9(1):40-48. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10018-1294. Euroasian J Hepatogastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31988866 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Optimization of diagnostic ultrasonography of the gallbladder based on own experience and literature.J Ultrason. 2020;20(80):e29-e35. doi: 10.15557/JoU.2020.0006. Epub 2020 Mar 31. J Ultrason. 2020. PMID: 32320550 Free PMC article.
-
Gallbladder polyps: Correlation of size and clinicopathologic characteristics based on updated definitions.PLoS One. 2020 Sep 11;15(9):e0237979. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237979. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32915805 Free PMC article.
-
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy for Gallbladder Dysfunction and Polyps: Incidence and Follow up.JSLS. 2021 Apr-Jun;25(2):e2021.00009. doi: 10.4293/JSLS.2021.00009. JSLS. 2021. PMID: 33981137 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Factors and Prognostic Factors in GBC.J Clin Med. 2024 Jul 18;13(14):4201. doi: 10.3390/jcm13144201. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39064241 Free PMC article. Review.
-
UIdataGB: Multi-Class ultrasound images dataset for gallbladder disease detection.Data Brief. 2024 Apr 15;54:110426. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2024.110426. eCollection 2024 Jun. Data Brief. 2024. PMID: 38708300 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Christensen AH, Ishak KG. Benign tumors and pseudotumors of the gallbladder. Report of 180 cases. Arch Pathol 1970;90:423-32. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials