Preparation of a nitric oxide imaging agent from gelatin derivative micelles
- PMID: 31245503
- PMCID: PMC6581831
- DOI: 10.1016/j.reth.2016.08.003
Preparation of a nitric oxide imaging agent from gelatin derivative micelles
Abstract
Introduction: Nitric oxide (NO) is an intracellular and intercellular messenger that plays an important role in cellular events in physiological and pathophysiological processes. NO is one of the inflammation markers and macrophages of an inflammatory cell produce a large amount of NO compared with other cells. Non-invasive detection system of NO is highly required to realize an early therapeutic treatment considering the process of pathophysiological changes. The objective of this study is to develop an imaging agent of nitric oxide (NO).
Methods: A water-insoluble DAR-4M of fluorescent dye for NO was solubilized in water through the micelle formation with gelatin grafted with l-α-phosphatidylethanolamine distearoyl (DAR-4M micelles). Physicochemical and biological properties of DAR-4M micelles were investigated by using cultured cells and animals.
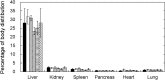
Results: The DAR-4M micelles responded to NO secreted from a NO donors, in contrast to the same concentration of free DAR-4M. When RAW264.7 of a macrophage cell line was stimulated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to allow them to generate NO, the DAR-4M micelles could detect NO of the cells to a significant great extent compared with free DAR-4M. After the intravenous injection of DAR-4M micelles or free DAR-4M to a mouse model of aristolochic acid (AA) induced acute interstitial nephritis, the DAR-4M micelles enhanced the fluorescence intensity from the kidneys to a significant great extent compared with the free DAR-4M injection. In case of DAR-4M micelles injection into normal mice, such an enhanced kidney fluorescence was not observed. A body distribution experiment demonstrated that the kidney accumulation of DAR-4M micelles was not modified by the AA-induced inflammation. After the AA injection, the number of CD11b-positive cells increased with time, indicating the increased number of inflammatory macrophages.
Conclusion: DAR-4M micelles are effective in imaging NO generated from macrophages accompanied with inflammation.
Keywords: Fluorescent dye; Gelatin; Macrophages; Nitric oxide; Polymer micelles; Water-solubilization.
Figures
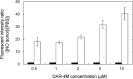
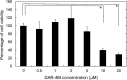
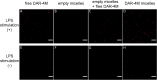
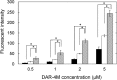
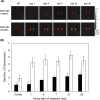
 ). The LPS concentration is 100 ng/ml. The DAR-4M micelles were prepared by DSPE-10. *p < 0.05; significance between the two groups.
). The LPS concentration is 100 ng/ml. The DAR-4M micelles were prepared by DSPE-10. *p < 0.05; significance between the two groups.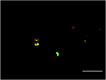
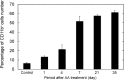
 ), 7 days (
), 7 days ( ), 21 days (
), 21 days ( ) and 35 days (
) and 35 days ( ) after injection.
) after injection.References
-
- Crupi A., Costa A., Tarnok A., Melzer S., Teodori L. Inflammation in tissue engineering: the Janus between engraftment and rejection. Eur J Immunol. 2015;45:3222–3236. - PubMed
-
- Palmer R.M., Ferrige A.G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987;327:524–526. - PubMed
-
- Furchgott R.F. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor: discovery, early studies, and identifcation as nitric oxide (Nobel lecture) Angew Chem Int Ed. 1999;38:1870–1880. - PubMed
-
- Murad F. Discovery of some of the biological effects of nitric oxide and its role in cell signaling (Nobel lecture) Angew Chem Int Ed. 1999;38:1857–1868. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

