LADDERS: A dynamic paradigm for planning, implementing, and evaluating sustainable change in learning health systems
- PMID: 31245586
- PMCID: PMC6508793
- DOI: 10.1002/lrh2.10058
LADDERS: A dynamic paradigm for planning, implementing, and evaluating sustainable change in learning health systems
Abstract
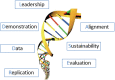
The science of learning health systems borrows and adapts models from many fields. One in particular is implementation science which has been experiencing a flourishing of new theories, models, and frameworks, some of which are generating sufficient evidence as to their effectiveness and applicability to emerge as candidates for wide adoption as useful tools for the field. In reviewing these, a common paradigm can be described which is a synthesis of those elements regularly cited by health systems implementing successful transformational change activities. As a paradigm, it offers a practical bridge to these models, concepts, and frameworks that are often hard to operationalize and are used with varying degrees of completeness. These elements can be arranged in a memorable acronym-LADDERS-Leadership, Alignment, Data, Demonstration, Evaluation, Replication, and Sustainability. LADDERS identifies the multiple elements and dimensions recognized by persons involved in leading health system change activities. It provides a simple, useful way to assess progress by health systems in planning, implementing, evaluating, and sustaining change. There is ample organizational and systems change literature to fully describe the actual LADDERS elements individually; therefore, this article describes characteristics and functions of each element and the dynamics represented in a DNA image to reflect that in learning health systems change is recursive, constant, and happens in complex environments that are always readjusting to new stimuli and directions, and this is often not accounted for in a framework, model, or theory. It concludes with several examples of application of the LADDERS paradigm and suggests how it is a complementary approach to accomplishing Institute of Medicine Learning Health Systems goals.
Keywords: change paradigm; dynamic tool; implementation science.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Sales A. Theory and frameworks in implementation research: current and future challenges 9th Annual Conference on the Science of Dissemination and Implementation In Health: Academy Health and NIH; 2017. [Available from: https://academyhealth.confex.com/academyhealth/2016di/meetingapp.cgi/Pap....
-
- Shmoop . Levels of organization and DNA structure, replication, and technology November 11, 2008. [cited 2008 November 11]. Available from: https://www.shmoop.com/dna/levels‐organization.html.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials