Diurnal regulation of cyanogenic glucoside biosynthesis and endogenous turnover in cassava
- PMID: 31245705
- PMCID: PMC6508492
- DOI: 10.1002/pld3.38
Diurnal regulation of cyanogenic glucoside biosynthesis and endogenous turnover in cassava
Abstract
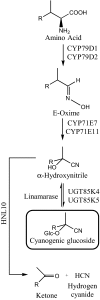
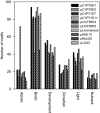
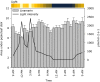
Cyanogenic glucosides are present in many plants, including eudicots, monocots, and ferns and function as defence compounds based on their ability to release hydrogen cyanide. In this study, the diurnal rhythm of cyanogenic glucoside content and of transcripts and enzymes involved in their biosynthesis was monitored in cassava plants grown in a glasshouse under natural light conditions. Transcripts of CYP79D1, CYP79D2, CYP71E7/11, and UGT85K5 were at minimal levels around 9 p.m., increased during the night and decreased following onset of early morning light. Transcripts of UGT85K4 and HNL10 showed more subtle variations with a maximum reached in the afternoon. Western blots showed that the protein levels of CYP71E7/11 and UGT85K4/5 decreased during the light period to a near absence around 4 p.m. and then recovered during the dark period. Transcript and protein levels of linamarase were stable throughout the 24-hr cycle. The linamarin content increased during the dark period. In the light period, spikes in the incoming solar radiation were found to result in concomitantly reduced linamarin levels. In silico studies of the promoter regions of the biosynthetic genes revealed a high frequency of light, abiotic stress, and development-related transcription factor binding motifs. The synthesis and endogenous turnover of linamarin are controlled both at the transcript and protein levels. The observed endogenous turnover of linamarin in the light period may offer a source of reduced nitrogen to balance photosynthetic carbon fixation. The rapid decrease in linamarin content following light spikes suggests an additional function of linamarin as a ROS scavenger.
Keywords: Manihot esculenta; UDPG‐dependent glycosyltransferase; biosynthesis; cytochrome P450; enzyme turnover; linamarin; lotaustralin; pathway regulation; transcriptional regulation.
Figures


References
-
- Akaracharanya, A. , Kesornsit, J. , Leepipatpiboon, N. , Srinorakutara, T. , Kitpreechavanich, V. , & Tolieng, V. (2011). Evaluation of the waste from cassava starch production as a substrate for ethanol fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae . Annuals of Microbiology, 61(3), 431–436. 10.1007/s13213-010-0155-8 - DOI
-
- Andersen, M. D. , Busk, P. K. , Svendsen, I. , & Møller, B. L. (2000). Cytochromes P‐450 from cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) catalyzing the first steps in the biosynthesis of the cyanogenic glucosides linamarin and lotaustralin – Cloning, functional expression in Pichia pastoris, and substrate specificity of the isolated recombinant enzymes. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275(3), 1966–1975. 10.1074/jbc.275.3.1966 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Blomstedt, C. K. , Gleadow, R. M. , O'Donnell, N. , Naur, P. , Jensen, K. , Laursen, T. , … Neale, A. D. (2012). A combined biochemical screen and TILLING approach identifies mutations in Sorghum bicolor L. Moench resulting in acyanogenic forage production. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 10(1), 54–66. 10.1111/j.1467-7652.2011.00646.x - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

