Improved renal outcomes after revascularization of the stenotic renal artery in pigs by prior treatment with low-energy extracorporeal shockwave therapy
- PMID: 31246892
- PMCID: PMC7304646
- DOI: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000002158
Improved renal outcomes after revascularization of the stenotic renal artery in pigs by prior treatment with low-energy extracorporeal shockwave therapy
Abstract
Background: Revascularization does not restore renal function in most patients with atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis (RAS), likely because of inflammation and fibrosis within the stenotic kidney. Low-energy shockwave therapy (LE-SWT) stimulates angiogenesis in the stenotic kidney, but its ability to improve renal function and structure after revascularization remains unexplored. We tested the hypothesis that a LE-SWT regimen before percutaneous transluminal renal angioplasty (PTRA) would enable PTRA to restore renal function in hypercholesterolemic pigs with RAS (HC+RAS), and that this would be associated with attenuation of renal inflammation and fibrosis.
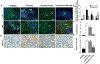
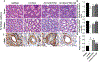
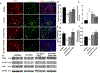
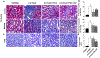
Methods and results: Twenty-six pigs were studied after 16 weeks of HC+RAS, HC+RAS treated with PTRA with or without a preceding LE-SWT regimen (bi-weekly for 3 weeks), and controls. Single-kidney renal blood flow (RBF), glomerular filtration rate (GFR), and oxygenation were assessed in vivo using imaging 4 weeks after PTRA, and then inflammation and fibrosis ex vivo.Four weeks after successful PTRA, blood pressure fell similarly in both revascularized groups. Yet, stenotic-kidney GFR remained lower in HC+RAS and HC+RAS+PTRA (P < 0.01 vs. normal), but was improved in HC+RAS+PTRA+SW (P > 0.05 vs. normal). Furthermore, reduced inflammation, medullary fibrosis, and cortical hypoxia were only shown in swine stenotic kidneys pretreated with LE-SWT before PTRA 4 weeks later.
Conclusion: LE-SWT delivery before revascularization permitted PTRA to improve function and decrease cortical and medullary damage in the stenotic swine kidney. This study, therefore, supports the use of an adjunct SW pretreatment to enhance the success of PTRA in blunting loss of kidney function in experimental HC+RAS.
Figures

Comment in
-
Improving intrarenal microcirculation prior to balloon angioplasty: new chances for the treatment of atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis?J Hypertens. 2019 Oct;37(10):1963-1965. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000002167. J Hypertens. 2019. PMID: 31464862 No abstract available.
-
Renal angioplasty deteriorated the outcome of shockwave therapy for atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis.J Hypertens. 2019 Nov;37(11):2301-2302. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000002240. J Hypertens. 2019. PMID: 31567760 No abstract available.
-
Reply.J Hypertens. 2019 Nov;37(11):2302-2303. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000002242. J Hypertens. 2019. PMID: 31567761 No abstract available.
References
-
- Fukumoto Y, Ito A, Uwatoku T, Matoba T, Kishi T, Tanaka H, et al. Extracorporeal cardiac shock wave therapy ameliorates myocardial ischemia in patients with severe coronary artery disease. Coron Artery Dis 2006; 17 (1):63–70. - PubMed
-
- Wang CJ, Huang KE, Sun YC, Yang YJ, Ko JY, Weng LH, et al. VEGF modulates angiogenesis and osteogenesis in shockwave-promoted fracture healing in rabbits. J Surg Res 2011; 171 (1):114–119. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

