A novel direct co-culture assay analyzed by multicolor flow cytometry reveals context- and cell type-specific immunomodulatory effects of equine mesenchymal stromal cells
- PMID: 31247035
- PMCID: PMC6597077
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218949
A novel direct co-culture assay analyzed by multicolor flow cytometry reveals context- and cell type-specific immunomodulatory effects of equine mesenchymal stromal cells
Abstract
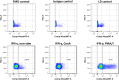
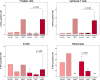
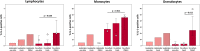
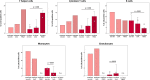
The immunomodulatory potential of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells (MSC) provides a basis for current and future regenerative therapies. In this study, we established an approach that allows to address the effects of pro-inflammatory stimulation and co-culture with MSC on different specific leukocyte subpopulations. Equine peripheral blood leukocyte recovery was optimized to preserve all leukocyte subpopulations and leukocyte activation regimes were evaluated. Allogeneic labeled equine adipose-derived MSC were then subjected to direct co-culture with either non-stimulated, concanavalin A (ConA)-activated or phosphate 12-myristate 13-acetate and ionomycin (PMA/I)-activated leukocytes. Subsequently, production of the cytokines interferon-γ (IFN- γ), interleukin-1 (IL-1) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and presence of FoxP3 were determined in specific cell populations using multicolor flow cytometry. Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) was measured in the supernatants. ConA-stimulation induced mild activation of leukocytes, whereas PMA/I-stimulation led to strong activation. In T cells, PMA/I promoted production of all cytokines, with no distinct suppressive effects of MSC. However, increased numbers of CD25/FoxP3-positive cells indicated that MSC supported regulatory T cell differentiation in PMA/I-activated leukocyte cultures. MSC also reduced numbers of cytokine-producing B cells and granulocytes, mostly irrespective of preceding leukocyte activation, and reversed the stimulatory effect of ConA on IFN-γ production in monocytes. Illustrating the possible suppressive mechanisms, higher numbers of MSC produced IL-10 when co-cultured with non-stimulated or ConA-activated leukocytes. This was not observed in co-culture with PMA/I-activated leukocytes. However, PGE2 concentration in the supernatant was highest in the co-culture with PMA/I-activated leukocytes, suggesting that PGE2 could still mediate modulatory effects in strongly inflammatory environment. These context- and cell type-specific modulatory effects observed give insight into the interactions between MSC and different types of immune cells and highlight the roles of IL-10 and PGE2 in MSC-mediated immunomodulation. The approach presented could provide a basis for further functional MSC characterization and the development of potency assays.
Conflict of interest statement
This work has no affiliation to the company Vaxxinova GmbH diagnostics. There are no competing interests. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures



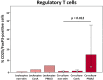
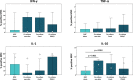

References
-
- Galipeau J, Krampera M, Barrett J, Dazzi F, Deans RJ, DeBruijn J, et al. International Society for Cellular Therapy perspective on immune functional assays for mesenchymal stromal cells as potency release criterion for advanced phase clinical trials. Cytotherapy. 2016;18:151–9. 10.1016/j.jcyt.2015.11.008 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

