Recent Advances in Biotransformation of Saponins
- PMID: 31248032
- PMCID: PMC6650892
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24132365
Recent Advances in Biotransformation of Saponins
Abstract
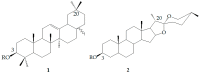
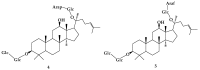
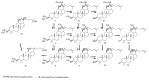
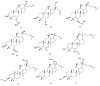
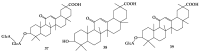
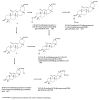
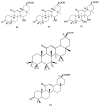
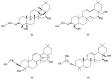
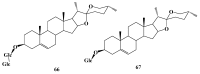
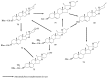
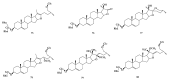
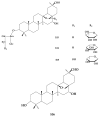
Saponins are a class of glycosides whose aglycones can be either triterpenes or helical spirostanes. It is commonly recognized that these active ingredients are widely found in various kinds of advanced plants. Rare saponins, a special type of the saponins class, are able to enhance bidirectional immune regulation and memory, and have anti-lipid oxidation, anticancer, and antifatigue capabilities, but they are infrequent in nature. Moreover, the in vivo absorption rate of saponins is exceedingly low, which restricts their functions. Under such circumstances, the biotransformation of these ingredients from normal saponins-which are not be easily adsorbed by human bodies-is preferred nowadays. This process has multiple advantages, including strong specificity, mild conditions, and fewer byproducts. In this paper, the biotransformation of natural saponins-such as ginsenoside, gypenoside, glycyrrhizin, saikosaponin, dioscin, timosaponin, astragaloside and ardipusilloside-through microorganisms (Aspergillus sp., lactic acid bacteria, bacilli, and intestinal microbes) will be reviewed and prospected.
Keywords: bioavailability; biotransformation; microorganisms; saponins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Haralampidis K., Trojanowska M., Osbourn A. Biosynthesis of triterpenoid saponins in plants. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2002;75:31–49. - PubMed
-
- Cheeke P.R. Actual and Potential Applications of Yucca Schidigera and Quillaja Saponaria Saponins in Human and Animal Nutrition. Sapon. Food Feedstuffs Med. Plants. 2000;45:241–254.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

