Composition and In Vitro Effects of Cultivars of Humulus lupulus L. Hops on Cholinesterase Activity and Microbial Growth
- PMID: 31248112
- PMCID: PMC6627407
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11061377
Composition and In Vitro Effects of Cultivars of Humulus lupulus L. Hops on Cholinesterase Activity and Microbial Growth
Abstract
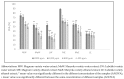
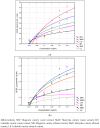
Common hop (Humulus lupulus L.) has significant health-promoting properties. Hop cones contain resins, essential oils, proteins, polyphenols, lipids, waxes, and cellulose. Hop extracts include bioactive compounds such as polyphenolic compounds (phenolic acids, and flavonols), and chlorophylls. The aim of this study was to compare the pro-health potential of hop cone extracts obtained from three cultivars (Magnum, Lubelski, and Marynka). The results showed that the cones of Magnum cultivar demonstrated the highest biological activity. The sum of phenolic acids and flavonols in ethanol extract was the highest for this variety and was equal 4903.5 µg/g dw. Ethanol extracts of Magnum cultivars showed the highest degree of iron ion chelation (55.43-88.76%) as well as the activity against 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl radical (4.75 mmol Tx/g dw). Hop cone extracts as cholinesterase inhibitors showed high potential for aqueous variants. In terms of antimicrobial activity, all investigated extracts demonstrated strong inhibition against Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis, with the Magnum cultivar showing the strongest inhibition. Owing to the biofunctional features of hop cone, it can be concluded that it is an attractive raw material with pro-health potential that can be used much more widely in food technology. However, it should be noted that toxicological tests and in vitro tests must be carried out before the raw material is used in food production.
Keywords: Humulus lupulus; antibacterial properties; flavonols; radical scavenging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antioxidant Activity of Humulus lupulus Phenolic Hop Extracts in Creating a New Pâté: An Element Affecting Fat Stability and Microbiological Quality during Storage.Molecules. 2024 Mar 31;29(7):1561. doi: 10.3390/molecules29071561. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38611840 Free PMC article.
-
Hop (Humulus lupulus L.) Phenolic Compounds Profile Depends on Cultivar and Plant Organ Maturity.Molecules. 2025 May 29;30(11):2365. doi: 10.3390/molecules30112365. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40509252 Free PMC article.
-
The extract from hop cones (Humulus lupulus) as a modulator of oxidative stress in blood platelets.Platelets. 2011;22(5):345-52. doi: 10.3109/09537104.2010.549597. Epub 2011 Feb 25. Platelets. 2011. PMID: 21351847
-
[Research progress of chemical constituents and pharmacological activities in Humulus lupulus].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017 May;42(10):1825-1829. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20170224.016. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29090538 Review. Chinese.
-
Hop Compounds: Extraction Techniques, Chemical Analyses, Antioxidative, Antimicrobial, and Anticarcinogenic Effects.Nutrients. 2019 Jan 24;11(2):257. doi: 10.3390/nu11020257. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 30678345 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biological Activity of Humulus Lupulus (L.) Essential Oil and Its Main Components Against Sitophilus granarius (L.).Biomolecules. 2020 Jul 25;10(8):1108. doi: 10.3390/biom10081108. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32722511 Free PMC article.
-
Formation of Prenylated Chalcone Xanthohumol Cocrystals: Single Crystal X-Ray Diffraction, Vibrational Spectroscopic Study Coupled with Multivariate Analysis.Molecules. 2019 Nov 21;24(23):4245. doi: 10.3390/molecules24234245. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31766540 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Morus alba leaf extract dose on lipid oxidation, microbiological stability, and sensory evaluation of functional liver pâtés during refrigerated storage.PLoS One. 2021 Dec 23;16(12):e0260030. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0260030. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34941877 Free PMC article.
-
Physicochemical Properties and Antioxidant Activity of Portuguese Craft Beers and Raw Materials.Molecules. 2022 Nov 18;27(22):8007. doi: 10.3390/molecules27228007. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36432109 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidants in Hops: Bioavailability, Health Effects and Perspectives for New Products.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jan 27;11(2):241. doi: 10.3390/antiox11020241. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35204124 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Almaguer C., Schönberger C., Gastl M., Arendt E.K., Becker T. Humulus lupulus—A story that begs to be told. A review. J. Inst. Brew. 2014;120:289–314. doi: 10.1002/jib.160. - DOI
-
- Abram V., Čeh B., Vidmar M., Hercezi M., Lazić N., Bucik V., Možina S.S., Košir I.J., Kač M., Demšar L., et al. A comparison of antioxidant and antimicrobial activity between hop leaves and hop cones. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015;64:124–134. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.11.008. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases