MicroRNA-325-3p protects the heart after myocardial infarction by inhibiting RIPK3 and programmed necrosis in mice
- PMID: 31248365
- PMCID: PMC6598367
- DOI: 10.1186/s12867-019-0133-z
MicroRNA-325-3p protects the heart after myocardial infarction by inhibiting RIPK3 and programmed necrosis in mice
Erratum in
-
Correction to: MicroRNA-325-3p protects the heart after myocardial infarction by inhibiting RIPK3 and programmed necrosis in mice.BMC Mol Biol. 2019 Aug 6;20(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12867-019-0136-9. BMC Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31387543 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Receptor-interacting serine-threonine kinase 3 (RIPK3)-mediated necroptosis has been implicated in the progression of myocardial infarction (MI), but the underlying mechanisms, particularly whether microRNAs (miRNAs) are involved, remain largely unknown.
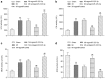
Results: A microarray analysis was used to screen for miR-325-3p expression in myocardial tissues from MI mice, and the expression was confirmed with qRT-PCR. The levels of myocardial enzymes were measured using commercial kits, and an echocardiography system was utilized for the detection of cardiac function parameters. The pathological features and infarction sizes of cardiac tissues were examined using H&E, TCC and Masson's trichrome staining, and the amount of cell apoptosis was determined using an in situ TUNEL assay. Cardiomyocytes were isolated and then subjected to hypoxia induction in vitro. The expression of the RIPK1, RIPK3 and phosphorylated MLKL (p-MLKL) proteins was measured using a Western blot. The mouse cardiomyocyte cell viability was analyzed by an MTT assay. The mRNA target of miR-325-3p was predicted using TargetScan v7.2 and then validated using a dual-luciferase reporter assay. The overexpression of miR-325-3p evidently decreased the expression levels of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), phosphocreatine kinase (CK), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and malondialdehyde (MDA), inhibited left ventricular end-diastolic diameter (LVEDD) and left ventricular end-systolic diameter (LVESD), and promoted left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and left ventricular fractional shortening (LVES). In addition, miR-325-3p overexpression attenuated the degree of injury to the cardiac tissue, decreased the infarct sizes and downregulated the expression of the necrosis-related proteins RIPK1, RIPK3 and p-MLKL.
Conclusions: The RIPK1/RIPK3/p-MLKL axis-induced necroptosis that occurred during MI was mediated by a miRNA module, miR-325-3p, which can effectively ameliorate the symptoms of MI by suppressing the expression of RIPK3.
Keywords: MiR-325-3p; Myocardial infarction; Necroptosis; RIPK3.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Lee ES, Vedanthan R, Jeemon P, Kamano JH, Kudesia P, Rajan V, Engelgau M, Moran AE. Quality improvement in cardiovascular disease care. In: Prabhakaran D, Anand S, Gaziano TA, Mbanya JC, Wu Y, Nugent R, editors. Cardiovascular, respiratory, and related disorders. Washington (DC); 2017. - PubMed
-
- Fiorito G, Guarrera S, Valle C, Ricceri F, Russo A, Grioni S, Mattiello A, Di Gaetano C, Rosa F, Modica F, et al. B-vitamins intake, DNA-methylation of one carbon metabolism and homocysteine pathway genes and myocardial infarction risk: the EPICOR study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2014;24(5):483–488. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2013.10.026. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

