The Multilingual Naming Test (MINT) as a Measure of Picture Naming Ability in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 31248465
- PMCID: PMC6757330
- DOI: 10.1017/S1355617719000560
The Multilingual Naming Test (MINT) as a Measure of Picture Naming Ability in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
Objective: The present study investigated the ability of the Multilingual Naming Test (MINT), a picture naming test recently added to the National Alzheimer's Coordinating Center's (NACC) Uniform Data Set neuropsychological test battery, to detect naming impairment (i.e., dysnomia) across stages of Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Method: Data from the initial administration of the MINT were obtained on NACC participants who were cognitively normal (N = 3,981) or diagnosed with mild cognitive impairment (N = 852) or dementia (N = 1,148) with presumed etiology of AD. Dementia severity was rated using the Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR) scale.
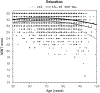
Results: Cross-sectional multiple regression analyses revealed significant effects of diagnostic group, sex, education, age, and race on naming scores. Planned comparisons collapsing across age and education groups revealed significant group differences in naming scores across levels of dementia severity. ROC curve analyses showed good diagnostic accuracy of MINT scores for distinguishing cognitively normal controls from AD dementia, but not from MCI. Within the cognitively normal group, there was a robust interaction between age and education such that naming scores exhibited the most precipitous drop across age groups for the least educated participants. Additionally, education effects were stronger in African-Americans than in Whites (a race-by-education interaction), and race effects were stronger in older than in younger age groups (a race-by-age interaction).
Conclusions: The MINT successfully detects naming deficits at different levels of cognitive impairment in patients with MCI or AD dementia, but comparison to age, sex, race, and education-corrected norms to determine impairment is essential.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Dysnomia; MCI; MINT; Naming.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
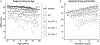

References
-
- Albert MS, DeKosky ST, Dickson D, Dubois B, Feldman HH, Fox NC, Gamst A, Holtzman DM, Jagust WJ, Petersen RC, Snyder PJ, Carrillo MC, Thies B, & Phelps CH (2011). The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 7, 270–279. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Albert MS, Heller HS, & Milberg W (1988). Changes in naming ability with age. Psychology and Aging, 3, 173–178. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JD (1988). The education of Blacks in the South, 1860–1935 Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P50 AG005142/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG049810/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016573/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG047266/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG025688/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005138/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG047366/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG019610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG028383/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG033514/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC011492/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013854/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG053760/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- F31 AG058379/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010124/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG023501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005131/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG072122/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG035982/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG008702/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG016976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG008051/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013846/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG047270/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062429/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005136/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG049638/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG012300/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005134/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG008017/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062715/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

