Mechanism of β2AR regulation by an intracellular positive allosteric modulator
- PMID: 31249059
- PMCID: PMC6705129
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aaw8981
Mechanism of β2AR regulation by an intracellular positive allosteric modulator
Abstract
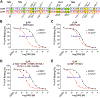
Drugs targeting the orthosteric, primary binding site of G protein-coupled receptors are the most common therapeutics. Allosteric binding sites, elsewhere on the receptors, are less well-defined, and so less exploited clinically. We report the crystal structure of the prototypic β2-adrenergic receptor in complex with an orthosteric agonist and compound-6FA, a positive allosteric modulator of this receptor. It binds on the receptor's inner surface in a pocket created by intracellular loop 2 and transmembrane segments 3 and 4, stabilizing the loop in an α-helical conformation required to engage the G protein. Structural comparison explains the selectivity of the compound for β2- over the β1-adrenergic receptor. Diversity in location, mechanism, and selectivity of allosteric ligands provides potential to expand the range of receptor drugs.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
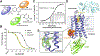
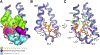

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

