Evaluation of Candida peritonitis with underlying peritoneal fibrosis and efficacy of micafungin in murine models of intra-abdominal candidiasis
- PMID: 31249356
- PMCID: PMC6597535
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-45776-x
Evaluation of Candida peritonitis with underlying peritoneal fibrosis and efficacy of micafungin in murine models of intra-abdominal candidiasis
Abstract
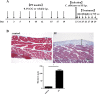
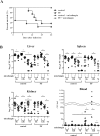
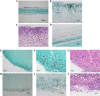
Candida peritonitis is a crucial disease, however the optimal antifungal therapy regimen has not been clearly defined. Peritoneal fibrosis (PF) can be caused by abdominal surgery, intra-abdominal infection, and malignant diseases, and is also widely recognized as a crucial complication of long-term peritoneal dialysis. However, the influence of PF on Candida peritonitis prognosis remains unknown. Here, we evaluated the severity of Candida peritonitis within the context of PF and the efficacy of micafungin using mice. A PF mouse model was generated by intraperitoneally administering chlorhexidine gluconate. Candida peritonitis, induced by intraperitoneal inoculation of Candida albicans, was treated with a 7-day consecutive subcutaneous administration of micafungin. Candida infection caused a higher mortality rate in the PF mice compared with the control mice on day 7. Proliferative Candida invasion into the peritoneum and intra-abdominal organs was confirmed pathologically only in the PF mice. However, all mice in both groups treated with micafungin survived until day 20. Micafungin treatment tends to suppress inflammatory cytokines in the plasma 12 h after infection in both groups. Our results suggest that PF enhances early mortality in Candida peritonitis. Prompt initiation and sufficient doses of micafungin had good efficacy for Candida peritonitis, irrespective of the underlying PF.
Conflict of interest statement
T.M. has received research grants from Astellas, Pfizer, MSD, and Asahi Kasei; K. Yamamoto and T.N. from MSD; K.I. and H.M. from Astellas, Pfizer, MSD, Sumitomo Dainippon, and Asahi Kasei; K. Yanagihara and S.K. from Astellas, Pfizer, MSD, Sumitomo Dainippon, Asahi Kasei, and Janssen. The remaining authors have no potential conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Figures

References
-
- Grassmann A, Gioberge S, Moeller S, Brown G. ESRD patients in 2004: global overview of patient numbers, treatment modalities and associated trends. Nephrology, dialysis, transplantation: official publication of the European Dialysis and Transplant Association - European Renal Association. 2005;20:2587–2593. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfi159. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shimaoka T, et al. Quantitative evaluation and assessment of peritoneal morphologic changes in peritoneal dialysis patients. Nephrology, dialysis, transplantation: official publication of the European Dialysis and Transplant Association - European Renal Association. 2010;25:3379–3385. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfq194. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

