Chronic kidney disease in propionic acidemia
- PMID: 31249402
- PMCID: PMC7045176
- DOI: 10.1038/s41436-019-0593-z
Chronic kidney disease in propionic acidemia
Abstract
Purpose: Propionic acidemia (PA) is a severe metabolic disorder characterized by multiorgan pathology, including renal disease. The prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in PA patients and factors associated with CKD in PA are not known.
Methods: Thirty-one subjects diagnosed with PA underwent laboratory and clinical evaluations through a dedicated natural history study at the National Institutes of Health (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT02890342).
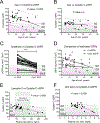
Results: Cross-sectional analysis of the creatinine-based estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) in subjects with native kidneys revealed an age-dependent decline in renal function (P < 0.002). Among adults with PA, 4/8 (50%) had eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2. There was a significant discrepancy between eGFRs calculated using estimating equations based on serum creatinine compared with serum cystatin C (P < 0.0001). The tubular injury marker, plasma lipocalin-2, and plasma uric acid were strongly associated with CKD (P < 0.0001). The measured 24-hour creatinine excretion was below normal, even after adjusting for age, height, and sex.
Conclusion: CKD is common in adults with PA and is associated with age. The poor predictive performance of standard eGFR estimating equations, likely due to reduced creatine synthesis in kidney and liver, could delay the recognition of CKD and management of ensuing complications in this population.
Keywords: GFR; chronic kidney disease; creatinine; cystatin C; propionic acidemia.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors have declared no conflicts of interest relevant to this work.
Figures
References
-
- Shchelochkov OA, Carrillo N, Venditti C. Propionic Acidemia. In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, et al., eds. GeneReviews((R)). Seattle (WA)1993.
-
- Kölker S, Valayannopoulos V, Burlina AB, et al. The phenotypic spectrum of organic acidurias and urea cycle disorders. Part 2: the evolving clinical phenotype. Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease. 2015;38(6):1059–1074. - PubMed
-
- Horster F, Baumgartner MR, Viardot C, et al. Long-term outcome in methylmalonic acidurias is influenced by the underlying defect (mut0, mut-, cblA, cblB). Pediatric research. 2007;62(2):225–230. - PubMed
-
- Lam C, Desviat LR, Perez-Cerda C, Ugarte M, Barshop BA, Cederbaum S. 45-Year-old female with propionic acidemia, renal failure, and premature ovarian failure; late complications of propionic acidemia? Molecular genetics and metabolism. 2011;103(4):338–340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

