2019 Consensus Statement of the Taiwan Hypertension Society and the Taiwan Society of Cardiology on Renal Denervation for the Management of Arterial Hypertension
- PMID: 31249454
- PMCID: PMC6533581
- DOI: 10.6515/ACS.201905_35(3).20190415A
2019 Consensus Statement of the Taiwan Hypertension Society and the Taiwan Society of Cardiology on Renal Denervation for the Management of Arterial Hypertension
Abstract
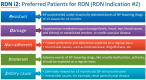
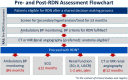
Sympathetic overactivity, an essential mechanism of hypertension, in driving sustained hypertension derives mostly from its effects on renal function. Percutaneous renal denervation (RDN) is designed to disrupt renal afferent and efferent sympathetic nerves to achieve sustained blood pressure (BP) reduction. Since 2017 onward, all three proof-of-concept, sham-controlled RDN trials demonstrated that RDN achieved consistent and clinically meaningful BP reductions [approximately 10 mmHg in office systolic BP (SBP) and 6-9 mmHg in 24-hour SBP] compared to sham operation in patients with mild to moderate or uncontrolled hypertension. There were no serious adverse events. The registry data in Taiwan showed similar 24-hour BP reductions at 12 months following RDN. The Task Force considers RDN as a legitimate alternative antihypertensive strategy and recommends 1) RDN should be performed in the context of registry and clinical studies (Class I, Level C) and 2) RDN should not be performed routinely, without detailed evaluation of various causes of secondary hypertension and renal artery anatomy (Class III, Level C). RDN could be performed in patients who fulfill either of the following BP criteria: 1) office BP ≥ 150/90 mmHg and daytime ambulatory SBP ≥ 135 mmHg or diastolic BP (DBP) ≥ 85 mmHg, irrespective of use of antihypertensive agents (Class IIa, Level B), or 2) 24-hour ambulatory SBP ≥ 140 mmHg and DBP ≥ 80 mmHg, irrespective of use of antihypertensive agents (Class IIa, Level B), with eligible renal artery anatomy and estimated glomerular filtration rate ≥ 45 mL/min/1.73 m2. Five subgroups of hypertensive patients are deemed preferred candidates for RDN and dubbed "RDN i2": Resistant hypertension, patients with hypertension-mediated organ Damage, Non-adherent to antihypertensive medications, intolerant to antihypertensive medications, and patients with secondary (2ndary) causes being treated for ≥ 3 months but BP still uncontrolled. The Task Force recommends assessment of three aspects, dubbed "RAS" (R for renal, A for ambulatory, S for secondary), beforehand to ascertain whether RDN could be performed appropriately: 1) Renal artery anatomy eligibility assessed by computed tomography or magnetic resonance renal angiography if not contraindicated, 2) genuine uncontrolled BP confirmed by 24-hour Ambulatory BP monitoring, and 3) Secondary hypertension identified and properly treated. After the procedure, 24-hour ambulatory BP monitoring, together with the dose and dosing interval of all BP-lowering drugs, should be obtained 6 months following RDN. Computed tomography or magnetic resonance renal angiography should be obtained 12 months following RDN, given that renal artery stenosis might not be clinically evident.
Keywords: Blood pressure; Catheter ablation; Hypertension; Nerve; Renal artery.
Figures

References
-
- Chiang CE, Wang TD, Ueng KC, et al. 2015 guidelines of the Taiwan Society of Cardiology and the Taiwan Hypertension Society for the management of hypertension. J Chin Med Assoc. 2015;78:1–47. - PubMed
-
- Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APHA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on clinical practice guidelines. Hypertension. 2018;71:e13–e115. - PubMed
-
- Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, et al. 2018 ESC/ESH guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2018;39:3021–3104. - PubMed
-
- Beaney T, Schutte AE, Tomaszewski M, et al. May measurement month 2017: an analysis of blood pressure screening results worldwide. Lancet Glob Health. 2018;6:e736–e743. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
