Transcriptome Profiling Reveals Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines and Matrix Metalloproteinase Activation in Zika Virus Infected Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells
- PMID: 31249527
- PMCID: PMC6582368
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00642
Transcriptome Profiling Reveals Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines and Matrix Metalloproteinase Activation in Zika Virus Infected Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells
Abstract
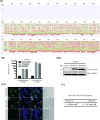
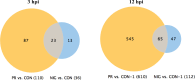
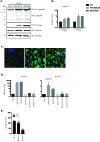
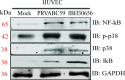
The deformities in the newborns infected with Zika virus (ZIKV) present a new potential public health threat to the worldwide community. Although ZIKV infection is mainly asymptomatic in healthy adults, infection during pregnancy can cause microcephaly and other severe brain defects and potentially death of the fetus. The detailed mechanism of ZIKV-associated damage is still largely unknown; however, it is apparent that the virus crosses the placental barrier to reach the fetus. Endothelial cells are the key structural component of the placental barrier. Endothelium integrity as semi-permeable barrier is essential to control the molecules and leukocytes trafficking across the placenta. Damaged endothelium or disruption of adherens junctions could compromise endothelial barrier integrity causing leakage and inflammation. Endothelial cells are often targeted by viruses, including the members of the Flaviviridae family such as dengue virus (DENV) and West Nile virus (WNV); however, little is known about the effects of ZIKV infection of endothelial cell functions. Our transcriptomic data have demonstrated that the large number of cytokines is affected in ZIKV-infected endothelial cells, where significant changes in 13 and 11 cytokines were identified in cells infected with PRVABC59 and IBH30656 ZIKV strains, respectively. Importantly, these cytokines include chemokines attracting mononuclear leukocytes (monocytes and lymphocytes) as well as neutrophils. Additionally, changes in matrix metalloproteinase (MMPs) were detected in ZIKV-infected cells. Furthermore, we for the first time showed that ZIKV infection of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) increases endothelial permeability. We reason that increased endothelial permeability was due to apoptosis of endothelial cells caused by caspase-8 activation in ZIKV-infected cells.
Keywords: Zika virus; cell permeability; cytokines; inflammation; matrix metalloproteinase.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Zika, dengue and yellow fever viruses induce differential anti-viral immune responses in human monocytic and first trimester trophoblast cells.Antiviral Res. 2018 Mar;151:55-62. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2018.01.003. Epub 2018 Jan 10. Antiviral Res. 2018. PMID: 29331320 Free PMC article.
-
Zika Virus Persistently Infects and Is Basolaterally Released from Primary Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells.mBio. 2017 Jul 11;8(4):e00952-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00952-17. mBio. 2017. PMID: 28698279 Free PMC article.
-
Sertoli Cells Are Susceptible to ZIKV Infection in Mouse Testis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Jun 21;7:272. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00272. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28680856 Free PMC article.
-
Zika Virus Transmission Through Blood Tissue Barriers.Front Microbiol. 2019 Jul 4;10:1465. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01465. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31333605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathways Exploited by Flaviviruses to Counteract the Blood-Brain Barrier and Invade the Central Nervous System.Front Microbiol. 2019 Mar 28;10:525. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00525. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30984122 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of Zika Virus Endocytic Pathways in Human Glioblastoma Cells.Front Microbiol. 2020 Mar 6;11:242. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00242. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32210929 Free PMC article.
-
Zika virus-induced neuro-ocular pathology in immunocompetent mice correlates with anti-ganglioside autoantibodies.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2020 Sep 1;16(9):2092-2108. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2020.1775459. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2020. PMID: 32758108 Free PMC article.
-
A Primer on Proteomic Characterization of Intercellular Communication in a Virus Microenvironment.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2025 Mar;24(3):100913. doi: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2025.100913. Epub 2025 Jan 23. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2025. PMID: 39862905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ZIKV Infection Induces DNA Damage Response and Alters the Proteome of Gastrointestinal Cells.Viruses. 2020 Jul 17;12(7):771. doi: 10.3390/v12070771. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32708879 Free PMC article.
-
Growth hormone attenuates the brain damage caused by ZIKV infection in mice.Virol Sin. 2022 Aug;37(4):601-609. doi: 10.1016/j.virs.2022.06.004. Epub 2022 Jun 15. Virol Sin. 2022. PMID: 35714850 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

