The Relationship Between Self-Control and Self-Efficacy Among Patients With Substance Use Disorders: Resilience and Self-Esteem as Mediators
- PMID: 31249535
- PMCID: PMC6582546
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00388
The Relationship Between Self-Control and Self-Efficacy Among Patients With Substance Use Disorders: Resilience and Self-Esteem as Mediators
Abstract
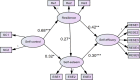
Background: While substance use disorder is one of the overarching health and social issues that might seriously disrupt individuals' self-control and self-efficacy, most previous studies have been conducted among university students or other groups, and little is known about how the underlying mechanisms between self-control and self-efficacy might impact patients with substance use disorders. Objectives: The purpose of this study is to investigate how resilience and self-esteem mediate the relationships between self-control and self-efficacy among patients with substance use disorders. Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study of 298 patients with substance use disorder from Shifosi rehab in China. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (5th Edition)-based diagnostic questionnaires were used to collect demographic information and assess addiction severity. The Dual-Modes of Self-Control Scale (DMSC-S) was implemented to measure self-control, while self-esteem was measured using the Self-esteem Scale (SES). The Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale (CD-RISC) was used to measure resilience, and self-efficacy was measured by the regulatory emotional self-efficacy scale (RESE). Results: The correlations between all the dimensions and total scores on the self-control, resilience, self-esteem, and self-efficacy were significantly positive (p < 0.01), indicating that they could predict patients' self-efficacy. Bootstrap testing indicated that resilience and self-esteem fully mediated the relationship between self-control and self-efficacy, relationships between self-control and self-esteem were partially mediated by resilience, and resilience partially mediated the relationship between self-esteem and self-efficacy. Finally, the multiple-group analysis indicated that the relationships among self-control, resilience, self-esteem, and self-efficiency did not differ with respect to gender. Conclusions: The path from self-control through resilience and self-esteem and on to self-efficacy is significant among patients with substance use disorders, suggesting that increasing self-control, resilience, and self-esteem can improve self-efficacy among patients with substance use disorders.
Keywords: patients with substance use disorders; resilience; self-control; self-efficacy; self-esteem.
Figures

Similar articles
-
How Resilience Promotes Mental Health of Patients With DSM-5 Substance Use Disorder? The Mediation Roles of Positive Affect, Self-Esteem, and Perceived Social Support.Front Psychiatry. 2020 Dec 3;11:588968. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.588968. eCollection 2020. Front Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 33343422 Free PMC article.
-
Family Function Impacts Relapse Tendency in Substance Use Disorder: Mediated Through Self-Esteem and Resilience.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Feb 14;13:815118. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.815118. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35237192 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring self-esteem and personality traits as predictors of mental wellbeing among Chinese university students: the mediating and moderating role of resilience.Front Psychol. 2024 Apr 10;15:1308863. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1308863. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38659680 Free PMC article.
-
Childhood abuse and borderline personality disorder features in Chinese undergraduates: the role of self-esteem and resilience.BMC Psychiatry. 2021 Jul 1;21(1):326. doi: 10.1186/s12888-021-03332-w. BMC Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34210279 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of students with left-behind experiences on childhood: The relationship between negative life events and depression among college students in China.Int J Soc Psychiatry. 2018 Feb;64(1):56-62. doi: 10.1177/0020764017739332. Epub 2017 Nov 16. Int J Soc Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29145763
Cited by
-
The Mediating Effect of Self-Control on Depression and Tendencies of Eating Disorders in Adolescents.Front Psychiatry. 2021 Dec 17;12:690245. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.690245. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34975554 Free PMC article.
-
Resilience and relapse risk in Emirate adult patients with substance use disorder: a national cross-sectional study from the United Arab Emirates.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Sep 24;15:1444233. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1444233. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39381607 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Perceived Energy and Self-Beliefs for Physical Activity and Sports Activity of Patients With Multiple Sclerosis and Chronic Stroke.Front Psychol. 2021 Jan 28;11:570221. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.570221. eCollection 2020. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 33584409 Free PMC article.
-
Post-treatment life-trajectories among people who inject drugs who completed hepatitis C treatment with direct acting antivirals: A thematic analysis.Br J Health Psychol. 2025 Sep;30(3):e70005. doi: 10.1111/bjhp.70005. Br J Health Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40650350 Free PMC article.
-
Resilience and related factors as predictors of relapse risk in patients with substance use disorder: a cross-sectional study.Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2021 May 4;16(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s13011-021-00377-8. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2021. PMID: 33947412 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ford J, Blumenstein L. Self-control and substance use among college students. J Drug Issues (2012) 43(1):56–68. 10.1177/0022042612462216 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

