Positive Education Interventions Prevent Depression in Chinese Adolescents
- PMID: 31249543
- PMCID: PMC6582777
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01344
Positive Education Interventions Prevent Depression in Chinese Adolescents
Abstract
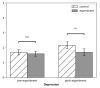
Positive education aims to improve students' academic performance as well as their well-being and character strengths. In contrast to traditional school counseling methods that are typically post hoc and pathological, positive education advocates a preventive and positive approach, which teaches students well-being skills that can reduce the chances of depression before it occurs. The current study tested this hypothesis by using a pseudo-experiment design. Six 8th grade classes (N = 173) in a Chinese school were randomly assigned into two groups. In the experiment group, students took positive education courses once a week that taught them primarily knowledge and skills related to positive emotions. Students in the control group took regular moral education courses. After one semester, the level of depression of students in the experiment group had no significant change while that of students in the control group increased significantly. The results showed that adolescent depression can be prevented by positive emotion interventions. Implications and limitations are discussed.
Keywords: China; adolescents; depression; intervention; positive education.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The influence of ambient aroma on middle school students' academic emotions.Int J Psychol. 2022 Jun;57(3):387-392. doi: 10.1002/ijop.12827. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Int J Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35060116 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Strengthened Physical Education on Academic Achievements in High School Students: A Quasi-Experiment in China.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Nov 25;16(23):4688. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16234688. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31775283 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the Maytiv positive psychology school program on early adolescents' well-being, engagement, and achievement.J Sch Psychol. 2016 Aug;57:73-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jsp.2016.05.003. Epub 2016 May 25. J Sch Psychol. 2016. PMID: 27425567 Clinical Trial.
-
Does narrative medicine education improve nursing students' empathic abilities and academic achievement? A randomised controlled trial.J Int Med Res. 2018 Aug;46(8):3306-3317. doi: 10.1177/0300060518781476. Epub 2018 Jul 6. J Int Med Res. 2018. PMID: 29976109 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of an educational intervention on HPV knowledge and attitudes towards HPV and its vaccines among junior middle school students in Chengdu, China.BMC Public Health. 2019 May 2;19(1):488. doi: 10.1186/s12889-019-6823-0. BMC Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31046722 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
School educational models and child mental health among K-12 students: a scoping review.Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. 2022 Apr 27;16(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s13034-022-00469-8. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. 2022. PMID: 35477408 Free PMC article.
-
Association between resilience and burnout of front-line nurses at the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic: Positive and negative affect as mediators in Wuhan.Int J Ment Health Nurs. 2021 Aug;30(4):939-954. doi: 10.1111/inm.12847. Epub 2021 Apr 23. Int J Ment Health Nurs. 2021. PMID: 33893718 Free PMC article.
-
Generation Z nursing students' online learning experiences during COVID-19 epidemic: A qualitative study.Heliyon. 2023 Apr;9(4):e14755. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14755. Epub 2023 Mar 22. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 36968654 Free PMC article.
-
School-based Psychosocial interventions on mental health among Chinese rural children with traumatic experiences: a protocol using cluster randomized controlled trial.BMC Psychol. 2023 May 4;11(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s40359-023-01182-7. BMC Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37143099 Free PMC article.
-
PERMA-based PBL teaching model: a case study of mechanical drawing in vocational education.Front Psychol. 2025 Jul 21;16:1536891. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1536891. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40761447 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adler A. (2016). Teaching well-being increases academic performance: Evidence from Bhutan. (Mexico, and Peru: University of Pennsylvania; ).
-
- Bagozzi R. P., Wong N., Yi Y. (1999). The role of culture and gender in the relationship between positive and negative affect. Cognit. Emot. 13, 641–672. 10.1080/026999399379023 - DOI
-
- Baumeister R. F., Bratslavsky E., Finkenauer C., Vohs K. D. (2001). Bad is stronger than good. Rev. Gen. Psychol. 5, 323–370. 10.1037/1089-2680.5.4.323 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources