Comparison of Apixaban and Low Molecular Weight Heparin in Preventing Deep Venous Thrombosis after Total Knee Arthroplasty in Older Adults
- PMID: 31250576
- PMCID: PMC6597473
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.7.626
Comparison of Apixaban and Low Molecular Weight Heparin in Preventing Deep Venous Thrombosis after Total Knee Arthroplasty in Older Adults
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the effect of apixaban and low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) in the prevention and treatment of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) after total knee arthroplasty in older adult patients.
Materials and methods: A total of 220 patients (average age of 67.8±6.4 years) undergoing total knee arthroplasty were randomly selected as research subjects and were divided into apixaban and LMWH groups (110 in each group).
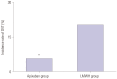
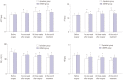
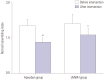
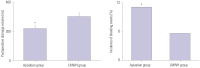
Results: The incidence of DVT was lower in the apixaban group than in the LMWH group (5.5% vs. 20.0%, p=0.001). Activated partial thromboplastin times (35.2±3.6 sec vs. 33.7±2.2 sec, p=0.010; 37.8±4.6 sec vs. 34.1±3.2 sec, p<0.001; 39.6±5.1 sec vs. 35.7±3.0 sec, p=0.032) and prothrombin times (14.0±1.0 sec vs. 12.8±0.9 sec, p<0.001; 14.5±1.2 sec vs. 13.0±1.1 sec, p<0.001; 15.3±1.4 sec vs. 13.2±1.3 sec, p=0.009) in the apixaban group at 1 week after surgery, 3 weeks after surgery, and the end of treatment were higher than those in the LMWH group. Platelet and fibrinogen levels in the apixaban group were lower than those of the LMWH group. Also, capillary plasma viscosity and erythrocyte aggregation in the apixaban group at 1 week after surgery, 3 weeks after surgery, and the end of treatment were lower than those in the LMWH group.
Conclusion: Apixaban, which elicits fewer adverse reactions and is safer than LMWH, exhibited better effects in the prevention and treatment of DVT after total knee arthroplasty in older adults.
Keywords: Apixaban; deep venous thrombosis; low molecular weight heparin; total knee arthroplasty.
© Copyright: Yonsei University College of Medicine 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Falck-Ytter Y, Francis CW, Johanson NA, Curley C, Dahl OE, Schulman S, et al. Prevention of VTE in orthopedic surgery patients. Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(2 Suppl):e278S–e325S. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wakabayashi H, Hasegawa M, Niimi R, Yamaguchi T, Naito Y, Sudo A. The risk factor of preoperative deep vein thrombosis in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Sci. 2017;22:698–702. - PubMed
-
- Zou Y, Tian S, Wang Y, Sun K. Administering aspirin, rivaroxaban and low-molecular-weight heparin to prevent deep venous thrombosis after total knee arthroplasty. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2014;25:660–664. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

