Influence of Environmental and Genetic Factors on Proteomic Profiling of Outer Membrane Vesicles from Campylobacter jejuni
- PMID: 31250596
- PMCID: PMC7256860
- DOI: 10.33073/pjm-2019-027
Influence of Environmental and Genetic Factors on Proteomic Profiling of Outer Membrane Vesicles from Campylobacter jejuni
Abstract
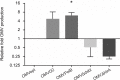
The proteomes of outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) secreted by C. jejuni 81-176 strain, which was exposed to oxygen or antibiotic stress (polymyxin B), were characterized. We also assessed the OMVs production and their content in two mutated strains - ∆dsbI and ∆htrA. OMVs production was significantly increased under the polymyxin B stress and remained unaltered in all other variants. Interestingly, the qualitative load of OMVs was constant regardless of the stress conditions or genetic background. However, certain proteins exhibited notable quantitative changes, ranging from 4-fold decrease to 10-fold increase. Up- or downregulated proteins (e.g. major outer membrane protein porA, iron ABC transporter, serine protease- htrA, 60 kDa chaperonin-groL, enolase) represented various cell compartments (cytoplasm, periplasm, and membrane) and exhibited various functions; nevertheless, one common group was noted that consisted of components of flagellar apparatus, i.e., FlaA/B, FlgC/E, which were mostly upregulated. Some of these proteins are the putative substrates of DsbI protein. Further investigation of the regulation of C. jejuni OMVs composition and their role in virulence will allow a better understanding of the infectious process of C. jejuni.
The proteomes of outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) secreted by C. jejuni 81–176 strain, which was exposed to oxygen or antibiotic stress (polymyxin B), were characterized. We also assessed the OMVs production and their content in two mutated strains – ∆dsbI and ∆htrA. OMVs production was significantly increased under the polymyxin B stress and remained unaltered in all other variants. Interestingly, the qualitative load of OMVs was constant regardless of the stress conditions or genetic background. However, certain proteins exhibited notable quantitative changes, ranging from 4-fold decrease to 10-fold increase. Up- or downregulated proteins (e.g. major outer membrane protein porA, iron ABC transporter, serine protease- htrA, 60 kDa chaperonin-groL, enolase) represented various cell compartments (cytoplasm, periplasm, and membrane) and exhibited various functions; nevertheless, one common group was noted that consisted of components of flagellar apparatus, i.e., FlaA/B, FlgC/E, which were mostly upregulated. Some of these proteins are the putative substrates of DsbI protein. Further investigation of the regulation of C. jejuni OMVs composition and their role in virulence will allow a better understanding of the infectious process of C. jejuni.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not report any financial or personal connections with other persons or organizations, which might negatively affect the contents of this publication and/or claim authorship rights to this publication.
Figures
References
-
- Bakun M, Karczmarski J, Poznanski J, Rubel T, Rozga M, Malinowska A, Sands D, Hennig E, Oledzki J, Ostrowski J, et al.. An integrated LC-ESI-MS platform for quantitation of serum peptide ladders. Application for colon carcinoma study. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2009. Aug;3(8):932–946. doi: 10.1002/prca.200800111 Medline - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

