Subclinical atherosclerosis and its progression are modulated by PLIN2 through a feed-forward loop between LXR and autophagy
- PMID: 31251843
- PMCID: PMC6899829
- DOI: 10.1111/joim.12951
Subclinical atherosclerosis and its progression are modulated by PLIN2 through a feed-forward loop between LXR and autophagy
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum.J Intern Med. 2021 Dec;290(6):1278. doi: 10.1111/joim.13365. Epub 2021 Sep 10. J Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 34506682 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Hyperlipidaemia is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease, and atherosclerosis is the underlying cause of both myocardial infarction and stroke. We have previously shown that the Pro251 variant of perilipin-2 reduces plasma triglycerides and may therefore be beneficial to reduce atherosclerosis development.
Objective: We sought to delineate putative beneficial effects of the Pro251 variant of perlipin-2 on subclinical atherosclerosis and the mechanism by which it acts.
Methods: A pan-European cohort of high-risk individuals where carotid intima-media thickness has been assessed was adopted. Human primary monocyte-derived macrophages were prepared from whole blood from individuals recruited by perilipin-2 genotype or from buffy coats from the Karolinska University hospital blood central.
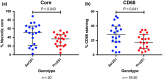
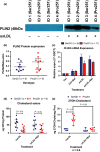
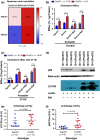
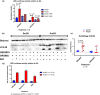
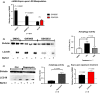
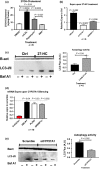
Results: The Pro251 variant of perilipin-2 is associated with decreased intima-media thickness at baseline and over 30 months of follow-up. Using human primary monocyte-derived macrophages from carriers of the beneficial Pro251 variant, we show that this variant increases autophagy activity, cholesterol efflux and a controlled inflammatory response. Through extensive mechanistic studies, we demonstrate that increase in autophagy activity is accompanied with an increase in liver-X-receptor (LXR) activity and that LXR and autophagy reciprocally activate each other in a feed-forward loop, regulated by CYP27A1 and 27OH-cholesterol.
Conclusions: For the first time, we show that perilipin-2 affects susceptibility to human atherosclerosis through activation of autophagy and stimulation of cholesterol efflux. We demonstrate that perilipin-2 modulates levels of the LXR ligand 27OH-cholesterol and initiates a feed-forward loop where LXR and autophagy reciprocally activate each other; the mechanism by which perilipin-2 exerts its beneficial effects on subclinical atherosclerosis.
Keywords: 27OH-cholesterol; PLIN2; atherosclerosis; autophagy; liver-X-receptor.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Internal Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Association for Publication of The Journal of Internal Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests pertaining the present study. The manuscript has been handled by an external editor, Professor of Medicine Sam Schulman, Mac Master University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada.
Figures
References
-
- Libby P, Ridker PM, Hansson GK. Progress and challenges in translating the biology of atherosclerosis. Nature 2011; 473: 317–25. - PubMed
-
- Buers I,Hofnagel O, Ruebel A, Severs NJ, Robenek H Lipid droplet associated proteins: an emerging role in atherogenesis. Histol Histopathol 2011; 26: 631–42. - PubMed
-
- Larigauderie G, Furman C, Jaye M et al. Adipophilin enhances lipid accumulation and prevents lipid efflux from THP‐1 macrophages: potential role in atherogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2004; 24: 504–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

