Revision of meso-Rex bypass utilizing a collateral vein in a patient with portal steal phenomenon after liver transplant: A case report
- PMID: 31252380
- PMCID: PMC6600796
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2019.05.051
Revision of meso-Rex bypass utilizing a collateral vein in a patient with portal steal phenomenon after liver transplant: A case report
Abstract
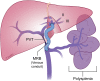
Introduction: In children with extrahepatic portal vein obstruction or those who develop portal vein thrombosis after liver transplant, the use of Meso-Rex Bypass (MRB) creates a more physiological state by redirecting mesenteric blood flow back into the intrahepatic portal system via a venous conduit.
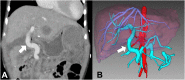
Presentation of case: A 3-year-old female with biliary atresia associated with polysplenia syndrome and a surgical history of Kasai portoenterostomy procedure, and an ABO incompatible whole liver transplant. Within a year after transplant she presented with prehepatic portal hypertension, that was treated with MRB using a deceased donor ABO compatible iliac vein as conduit. Six months later, she was taken to the operating room for bypass revision, during the procedure the MRB showed no flow and no thrombus, and a large splenorenal collateral vein that was causing a portal perfusion steal phenomenon was observed. After dissecting the collateral vein, an 8 cm x8 mm segment of this vessel was used as an autologous conduit to re-do the Rex.
Discussion: Failed of MRB can be attributed to portal steal phenomenon, hypercoagulable disorders, bypass contraction or kinking. In this case we believe the culprit to be the former. When there is a history of longstanding portal hypertension, large collaterals develop; thus, intraoperative portal vein flow measurement is critical and ligation of large collaterals during liver transplantation and MRB should be performed to avoid portal steal phenomenon postprocedure.
Conclusion: Using a collateral vein as an alternative autologous venous conduit is a feasible option that can have durable success.
Keywords: Collateral vein; Meso-Rex bypass; Pediatric liver transplantation; Portal steal phenomenon.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Tsochatzis E.A., Bosch J., Burroughs A.K. Liver cirrhosis. Lancet. 2014;383(May (9930)):1749–1761. - PubMed
-
- Shneider B.L., Bosch J., de Franchis R., Emre S.H., Groszmann R.J., Ling S.C. Portal hypertension in children: expert pediatric opinion on the report of the Baveno V Consensus Workshop on Methodology of Diagnosis and Therapy in Portal Hypertension. Pediatr. Transplant. 2012;16(August (5)):426–437. - PubMed
-
- Neto J.S., Fonseca E.A., Feier F.H., Pugliese R., Candido H.L., Benavides M.R. Analysis of factors associated with portal vein thrombosis in pediatric living donor liver transplant recipients. Liver Transpl. 2014;20(October (10)):1157–1167. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez F. Portal vein complications after pediatric liver transplantation. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2012;14(June (3)):270–274. - PubMed
-
- Bertocchini A., Falappa P., Grimaldi C., Bolla G., Monti L., de Ville de Goyet J. Intrahepatic portal venous systems in children with noncirrhotic prehepatic portal hypertension: anatomy and clinical relevance. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2014;49(August (8)):1268–1275. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

