Incidence and Cost of Acute Kidney Injury in Hospitalized Patients with Infective Endocarditis
- PMID: 31252690
- PMCID: PMC6678671
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm8070927
Incidence and Cost of Acute Kidney Injury in Hospitalized Patients with Infective Endocarditis
Abstract
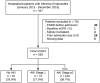
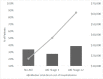
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a frequent complication of hospitalized patients with infective endocarditis (IE). Further, AKI in the setting of IE is associated with high morbidity and mortality. We aimed to examine the incidence, clinical parameters, and hospital costs associated with AKI in hospitalized patients with IE in an endemic area with an increasing prevalence of opioid use. This retrospective cohort study included 269 patients admitted to a major referral center in Kentucky with a primary diagnosis of IE from January 2013 to December 2015. Of these, 178 (66.2%) patients had AKI by Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) serum creatinine criteria: 74 (41.6%) had AKI stage 1 and 104 (58.4%) had AKI stage ≥2. In multivariable analysis, higher comorbidity scores and the need for diuretics were independently associated with AKI, while the involvement of the tricuspid valve and the need for vasopressor/inotrope support were independently associated with severe AKI (stage ≥2). The median total direct cost of hospitalization was progressively higher according to each stage of AKI ($17,069 for no AKI; $37,111 for AKI stage 1; and $61,357 for AKI stage ≥2; p < 0.001). In conclusion, two-thirds of patients admitted to the hospital due to IE had incident AKI. The occurrence of AKI significantly increased healthcare costs. The higher level of comorbidity, the affection of the tricuspid valve, and the need for diuretics and/or vasoactive drugs were associated with severe AKI in this susceptible population.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; healthcare costs; infective endocarditis; opioid use.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Murdoch D.R., Corey G.R., Hoen B., Miro J.M., Fowler V.G., Jr., Bayer A.S., Karchmer A.W., Olaison L., Pappas P.A., Moreillon P., et al. Clinical presentation, etiology, and outcome of infective endocarditis in the 21st century: The International Collaboration on Endocarditis-Prospective Cohort Study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009;169:463–473. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2008.603. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baddour L.M., Wilson W.R., Bayer A.S., Fowler V.G., Jr., Bolger A.F., Levison M.E., Ferrieri P., Gerber M.A., Tani L.Y., Gewitz M.H., et al. Infective endocarditis: Diagnosis, antimicrobial therapy, and management of complications: A statement for healthcare professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, and the Councils on Clinical Cardiology, Stroke, and Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia, American Heart Association: Endorsed by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Circulation. 2005;111:e394–e434. doi: 10.1161/circulationaha.105.165564. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pant S., Patel N.J., Deshmukh A., Golwala H., Patel N., Badheka A., Hirsch G.A., Mehta J.L. Trends in infective endocarditis incidence, microbiology, and valve replacement in the United States from 2000 to 2011. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015;65:2070–2076. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2015.03.518. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

