In silico analysis of missense mutations in exons 1-5 of the F9 gene that cause hemophilia B
- PMID: 31253089
- PMCID: PMC6599346
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-019-2919-x
In silico analysis of missense mutations in exons 1-5 of the F9 gene that cause hemophilia B
Abstract
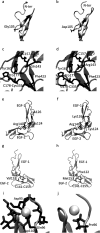
Background: Missense mutations in the first five exons of F9, which encodes factor FIX, represent 40% of all mutations that cause hemophilia B. To address the ongoing debate regarding in silico identification of disease-causing mutations at these exons, we analyzed 215 missense mutations from www.factorix.org using six in silico prediction tools, which are the most common used programs for analysis prediction of impact of mutations on the protein structure and function, with further advantage of using similar approaches. We developed different algorithms to integrate multiple predictions from such tools. In order to approach a structural analysis on FIX we performed a modeling of five selected pathogenic mutations.
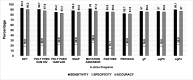
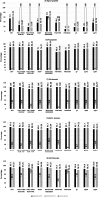
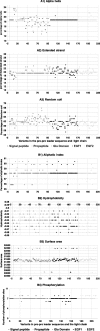
Results: SIFT, PolyPhen-2 HumDiv, SNAP2, and MutationAssessor were the most successful in identifying true non-causative and causative mutations. A proposed function integrating these algorithms (wgP4) was the most sensitive (90.1%), specific (22.6%), and accurate (87%) than similar functions, and identified 187 variants as deleterious. Clinical phenotype was significantly associated with predicted causative mutations at all five exons. However, PolyPhen-2 HumDiv was more successful in linking clinical severity to specific exons, while functions that integrate 4-6 predictions were more successful in linking phenotype to genotypes at the light chain (exons 3-5). The most important value of integrating multiple predictions is the inclusion of scores derived from different approaches. Modeling of protein structure showed the effects of pathogenic nsSNPs on structure and function of FIX.
Conclusions: A simple function that integrates information from different in silico programs yields the best prediction of mutated phenotypes. However, the specificity, sensitivity, and accuracy of genotype-phenotype predictions depend on specific characteristics of the protein domain and the disease of interest as we validated by the structural analysis of selected pathogenic F9 mutations. The proposed function integrating algorithm (wgP4) might be useful for the analysis of nsSNPs impact on other genes.
Keywords: F9 exons 1–5; Genotype-phenotype correlation; Hemophilia B; In silico analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
We have no competing interest at public or private institutions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Molecular Basis of FIX Deficiency in Hemophilia B.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 2;23(5):2762. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052762. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A new in silico approach to investigate molecular aspects of factor IX missense causative mutations and their impact on the hemophilia B severity.Hum Mutat. 2019 Jun;40(6):706-715. doi: 10.1002/humu.23733. Epub 2019 Mar 28. Hum Mutat. 2019. PMID: 30817849
-
In silico profiling of deleterious amino acid substitutions of potential pathological importance in haemophlia A and haemophlia B.J Biomed Sci. 2012 Mar 16;19(1):30. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-19-30. J Biomed Sci. 2012. PMID: 22423892 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the F9 genotype-specific FIX inhibitor risks and characterisation of 10 novel severe F9 defects in the first molecular series of Argentinian patients with haemophilia B.Thromb Haemost. 2013 Jan;109(1):24-33. doi: 10.1160/TH12-05-0302. Epub 2012 Oct 23. Thromb Haemost. 2013. PMID: 23093250 Free PMC article.
-
The Canadian "National Program for hemophilia mutation testing" database: a ten-year review.Am J Hematol. 2013 Dec;88(12):1030-4. doi: 10.1002/ajh.23557. Epub 2013 Sep 9. Am J Hematol. 2013. PMID: 23913812 Review.
Cited by
-
Computational approaches for predicting variant impact: An overview from resources, principles to applications.Front Genet. 2022 Sep 29;13:981005. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.981005. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36246661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Spectra of Disease-Causing Mutations in the Ferroportin 1 (SLC40A1) Encoding Gene and Related Iron Overload Phenotypes (Hemochromatosis Type 4 and Ferroportin Disease).Hum Mutat. 2023 Jun 13;2023:5162256. doi: 10.1155/2023/5162256. eCollection 2023. Hum Mutat. 2023. PMID: 40225168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Molecular Basis of FIX Deficiency in Hemophilia B.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 2;23(5):2762. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052762. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269902 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rallapalli P. M., Kemball-Cook G., Tuddenham E. G., Gomez K., Perkins S. J. An interactive mutation database for human coagulation factor IX provides novel insights into the phenotypes and genetics of hemophilia B. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 2013;11(7):1329–1340. doi: 10.1111/jth.12276. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

