Galcanezumab in episodic migraine: subgroup analyses of efficacy by high versus low frequency of migraine headaches in phase 3 studies (EVOLVE-1 & EVOLVE-2)
- PMID: 31253091
- PMCID: PMC6734504
- DOI: 10.1186/s10194-019-1024-x
Galcanezumab in episodic migraine: subgroup analyses of efficacy by high versus low frequency of migraine headaches in phase 3 studies (EVOLVE-1 & EVOLVE-2)
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Galcanezumab in episodic migraine: subgroup analyses of efficacy by high versus low frequency of migraine headaches in phase 3 studies (EVOLVE-1 & EVOLVE-2).J Headache Pain. 2019 Dec 27;20(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s10194-019-1069-x. J Headache Pain. 2019. PMID: 31881817 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Patients with high-frequency episodic migraine (HFEM) have a greater disease burden than those with low-frequency episodic migraine (LFEM). Acute treatment overuse increases the risk of migraine chronification in patients with HFEM. Galcanezumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody binding calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), is effective for migraine prevention with a favorable safety profile. Here, we investigate whether there are differences in galcanezumab efficacy in patients with LFEM or with HFEM.
Methods: Data were pooled from two double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trials; EVOLVE-1 and EVOLVE-2. Patients were 18-65 years old, experienced 4-14 monthly migraine headache days (MHDs) for ≥1 year prior, with onset at < 50 years of age. Migraine headaches were tracked via electronic patient-reported outcome system and randomization was stratified by low (LFEM; 4-7 monthly MHDs) or high (HFEM; 8-14 monthly MHDs) frequency. Subgroup analysis compared the HFEM and LFEM subgroups with a linear or generalized linear mixed model repeated measures approach.
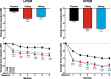
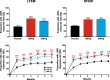
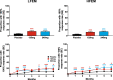
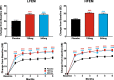
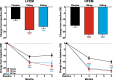
Results: The intent-to-treat patients (N = 1773) had a mean age of 41.3 years, were mostly white (75%), female (85%), and 66% of patients had HFEM. In both the LFEM and HFEM subgroups, the overall (Months 1-6) and monthly changes from baseline in monthly MHDs and monthly MHDs with acute medication use compared with placebo were statistically significantly reduced for galcanezumab 120-mg and 240-mg. Galcanezumab (120-mg and 240-mg) significantly decreased the overall and monthly MHDs with nausea and/or vomiting, and with photophobia and phonophobia versus placebo in patients with LFEM or HFEM. In both subgroups, the mean overall (Months 1-6) and monthly percentages of patients with ≥50%, ≥75%, and 100% reduction in monthly MHDs from baseline were statistically significantly greater in patients receiving either dose of galcanezumab versus placebo. Galcanezumab (120-mg and 240-mg) significantly improved the Migraine-Specific Quality of Life Questionnaire role function-restrictive domain score as well as the Migraine Disability Assessment total score versus placebo for patients with LFEM or HFEM. There were no significant subgroup-by-treatment interactions.
Conclusions: Galcanezumab was as effective in patients with HFEM as in those with LFEM. Associated symptoms, quality of life, and disability were similarly improved in patients with HFEM or LFEM.
Trial registration: NCT02614183 , NCT02614196 .
Keywords: Episodic migraine; Galcanezumab; Migraine frequency.
Conflict of interest statement
VLS and KD are full-time employees of Eli Lilly and Company and own stock in the company. SL is a full-time employee of Syneos Health. M-CW is a consultant and/or advisory panel member and have received honoraria from Allergan, Inc.; Amgen; electroCore Medical, LLC; Lilly USA, LLC; Teva Pharmaceuticals. SS is a consultant and/or advisory panel member and has received honoraria from Alder Biopharmaceuticals; Allergan, Inc.; Amgen; Avanir Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Cefaly; Curelator, Inc.; Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories; Egalet Corporation; eNeura Inc.; electroCore Medical, LLC; Lilly USA, LLC; Medscape, LLC.; NINDS; Satsuma Pharmaceuticals; Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Teva Pharmaceuticals; Theranica; and Trigemina, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017;390(10100):1211–59. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

