Mycophenolate Mofetil Versus Cyclophosphamide for the Induction of Remission in Nonlife-Threatening Relapses of Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis: Randomized, Controlled Trial
- PMID: 31253599
- PMCID: PMC6625631
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.11801018
Mycophenolate Mofetil Versus Cyclophosphamide for the Induction of Remission in Nonlife-Threatening Relapses of Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis: Randomized, Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background and objectives: Cyclophosphamide has been the mainstay of treatment of ANCA-associated vasculitis. However, cyclophosphamide has unfavorable side effects and alternatives are needed. Evidence suggests that mycophenolate mofetil can induce sustained remission in nonlife-threatening disease. The purpose of this study was to compare the efficacy and safety of mycophenolate mofetil versus cyclophosphamide for the induction treatment of nonlife-threatening relapses of proteinase 3-ANCA- and myeloperoxidase-ANCA-associated vasculitis.
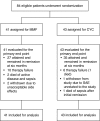
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: We conducted a multicenter randomized, controlled trial. Participants with a first or second relapse of ANCA-associated vasculitis were randomized to induction treatment with cyclophosphamide or mycophenolate mofetil both in combination with glucocorticoids. Maintenance therapy consisted of azathioprine in both arms. Primary outcome was remission at 6 months, and secondary outcomes included disease-free survival at 2 and 4 years.
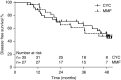
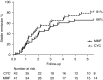
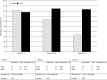
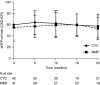
Results: Eighty-four participants were enrolled, of whom 41 received mycophenolate mofetil and 43 received cyclophosphamide. Eighty-nine percent of participants were proteinase 3-ANCA positive. At 6 months, 27 (66%) mycophenolate mofetil-treated participants versus 35 (81%) cyclophosphamide-treated participants were in remission (P=0.11). Disease-free survival rates at 2 and 4 years were 61% and 39% for cyclophosphamide, respectively, and 43% and 32% for mycophenolate mofetil, respectively (at 4 years, log rank test, P=0.17).
Conclusions: We did not demonstrate mycophenolate mofetil to be similarly effective as cyclophosphamide in inducing remission of relapsed ANCA-associated vasculitis. However, mycophenolate mofetil might be an alternative to cyclophosphamide for the treatment of selected patients with nonlife-threatening relapses.
Keywords: ANCA; Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis; Antibodies; Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic; Mycophenolic Acid; Recurrence; Remission Induction; cyclophosphamide; mycophenolate mofetil; randomized controlled trials; relapse; vasculitis.
Copyright © 2019 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Treatment of Relapses in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019 Jul 5;14(7):967-969. doi: 10.2215/CJN.06250519. Epub 2019 Jun 28. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31278112 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hoffman GS, Kerr GS, Leavitt RY, Hallahan CW, Lebovics RS, Travis WD, Rottem M, Fauci AS: Wegener granulomatosis: An analysis of 158 patients. Ann Intern Med 116: 488–498, 1992 - PubMed
-
- Joy MS, Hogan SL, Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Nachman PH: A pilot study using mycophenolate mofetil in relapsing or resistant ANCA small vessel vasculitis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 20: 2725–2732, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Hu W, Liu C, Xie H, Chen H, Liu Z, Li L: Mycophenolate mofetil versus cyclophosphamide for inducing remission of ANCA vasculitis with moderate renal involvement. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23: 1307–1312, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Han F, Liu G, Zhang X, Li X, He Q, He X, Li Q, Wang S, Wang H, Chen J: Effects of mycophenolate mofetil combined with corticosteroids for induction therapy of microscopic polyangiitis. Am J Nephrol 33: 185–192, 2011 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

