Hummingbird Study: a study protocol for a multicentre exploratory trial to assess the acceptance and performance of a digital medicine system in adults with schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder or first-episode psychosis
- PMID: 31253613
- PMCID: PMC6609081
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-025952
Hummingbird Study: a study protocol for a multicentre exploratory trial to assess the acceptance and performance of a digital medicine system in adults with schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder or first-episode psychosis
Abstract
Introduction: In patients with schizophrenia, medication adherence is important for relapse prevention, and effective adherence monitoring is essential for treatment planning. A digital medicine system (DMS) has been developed to objectively monitor patient adherence and support clinical decision making regarding treatment choices. This study assesses the acceptance and performance of the DMS in adults with schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder or first-episode psychosis and in healthcare professionals (HCPs).
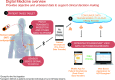
Methods/analysis: This is a multicentre, 8-week, single-arm, open-label pragmatic trial designed using coproduction methodology. The study will be conducted at five National Health Service Foundation Trusts in the UK. Patients 18-65 years old with a diagnosis of schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder or first-episode psychosis will be eligible. HCPs (psychiatrists, care coordinators, nurses, pharmacists), researchers, information governance personnel, clinical commissioning groups and patients participated in the study design and coproduction. Intervention employed will be the DMS, an integrated system comprising an oral sensor tablet coencapsulated with an antipsychotic, non-medicated wearable patch, mobile application (app) and web-based dashboard. The coencapsulation product contains aripiprazole, olanzapine, quetiapine or risperidone, as prescribed by the HCP, with a miniature ingestible event marker (IEM) in tablet. On ingestion, the IEM transmits a signal to the patch, which collects ingestion and physical activity data for processing on the patient's smartphone or tablet before transmission to a cloud-based server for viewing by patients, caregivers and HCPs on secure web portals or mobile apps.
Ethics and dissemination: Approval was granted by London - City and East Research Ethics Committee (REC ref no 18/LO/0128), and clinical trial authorisation was provided by the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency. Written informed consent will be obtained from every participant. The trial will be compliant with the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use guidelines and the Declaration of Helsinki.
Trial registration number: NCT03568500; EudraCT2017-004602-17; Pre-results.
Keywords: coproduction; digital medicine; schizoaffective disorder; schizophrenia.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2019. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: JCF, JK and TP-S are employees of Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization. NC is an employee of Otsuka Pharmaceutical Europe. AM is an employee of Otsuka Europe Development and Commercialisation. SR has received honoraria from Otsuka and Lundbeck for educational sessions.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. The Global Burden of Disease: 2004 update. 2008. http://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/GBD_report_2004updat... [Accessed 29 June 2018].
-
- Rathod S, Garner C, Griffiths A, et al. . Protocol for a multicentre study to assess feasibility, acceptability, effectiveness and direct costs of TRIumPH (Treatment and Recovery In PsycHosis): integrated care pathway for psychosis. BMJ Open 2016;6:e012751 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-012751 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hasan A, Falkai P, Wobrock T, et al. . World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) guidelines for biological treatment of schizophrenia, part 2: update 2012 on the long-term treatment of schizophrenia and management of antipsychotic-induced side effects. World J Biol Psychiatry 2013;14:2–44. 10.3109/15622975.2012.739708 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
