Role of Programmed Cell Death 4 (PDCD4)-Mediated Akt Signaling Pathway in Vascular Endothelial Cell Injury Caused by Lower-Extremity Ischemia-Reperfusion in Rats
- PMID: 31253757
- PMCID: PMC6613321
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.914035
Role of Programmed Cell Death 4 (PDCD4)-Mediated Akt Signaling Pathway in Vascular Endothelial Cell Injury Caused by Lower-Extremity Ischemia-Reperfusion in Rats
Abstract
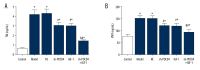
BACKGROUND We aimed to investigate the role of PDCD4-mediated Akt signaling pathway in vascular endothelial cell injury caused by ischemia-reperfusion in the lower extremities. MATERIAL AND METHODS Ten rats were used as control, while 50 rats were used for creating disease models and were assigned to 5 groups: model group (no injection), NC group (injected with vectors containing PDCD negative control sequence), sh-PDCD4 group (injected with vectors containing sh-PDCD4 sequence), IGF-1 group (injected with IGF-1), and sh-PDCD4+IGF-1 group (injected with IGF-1 and vectors containing sh-PDCD4 sequence). RESULTS Compared with the control group, the expression levels of PDCD4 mRNA and protein, as well as levels of circulating endothelial cells, von Willebrand factor, thrombomodulin, and malondialdehyde, increased in the other 5 groups, while the mRNA and protein expression levels of Akt and eNOS, the protein expression levels of p-Akt and p-eNOS, and superoxide dismutase content decreased in these groups (all P<0.05). Compared with the model group, the sh-PDCD4 and sh-PDCD4+1GF-1 groups had lower mRNA and protein expressions of PDCD4 (all P<0.05), whereas the IGF-1 group had similar levels (all P>0.05). These 3 groups had lower levels of circulating endothelial cells, von Willebrand factor, thrombomodulin, and malondialdehyde, and higher mRNA and protein expressions of Akt and eNOS, protein expressions of p-Akt and p-eNOS, and superoxide dismutase content (all P<0.05). The NC group did not differ from the model group (all P>0.05). CONCLUSIONS PDCD4 gene silencing can activate the Akt signaling pathway and attenuate vascular endothelial cell injury caused by ischemia-reperfusion in the lower extremities in rats.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Effect of microRNA-26a on vascular endothelial cell injury caused by lower extremity ischemia-reperfusion injury through the AMPK pathway by targeting PFKFB3.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Mar;234(3):2916-2928. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27108. Epub 2018 Aug 21. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30132885
-
MiR-340-5p alleviates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced neuronal injury via PI3K/Akt activation by targeting PDCD4.Neurochem Int. 2020 Mar;134:104650. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2019.104650. Epub 2019 Dec 20. Neurochem Int. 2020. PMID: 31870893
-
Protective role of microRNA-27a upregulation and HSP90 silencing against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by activating PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Sep;86:106635. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106635. Epub 2020 Jul 4. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. Retraction in: Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Oct;99:108032. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108032. PMID: 32634698 Retracted.
-
Progress on the relationship between tumor suppressor PDCD4 and diseases based on the analysis of structural characteristics.Yi Chuan. 2024 Apr 20;46(4):290-305. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.23-291. Yi Chuan. 2024. PMID: 38632092 Review.
-
The Impact of Pdcd4, a Translation Inhibitor, on Drug Resistance.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Oct 19;17(10):1396. doi: 10.3390/ph17101396. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39459035 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in the treatment of lower-extremity ischemia-reperfusion injury.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 23;16:1576091. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1576091. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40487397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma cell-free RNA signatures of inflammatory syndromes in children.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Sep 10;121(37):e2403897121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2403897121. Epub 2024 Sep 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39240972 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of miR-499a-5p Decreases Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Targeting PDCD4.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Oct;42(7):2157-2170. doi: 10.1007/s10571-021-01085-4. Epub 2021 Apr 9. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 33837492 Free PMC article.
-
WWP2 ameliorates oxidative stress and inflammation in atherosclerotic mice through regulation of PDCD4/HO-1 pathway.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2022 Aug 25;54(8):1057-1067. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2022091. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2022. PMID: 35983977 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Comu FM, Kilic Y, Ozer A, et al. Effect of Picroside-2 on erythrocyte deformability and lipid peroxidation in rats subjected to lower extremity ischemia-reperfusion injury. Acta Physiologica. 2015;215:71.
-
- Nagy T, Kovacs V, Hardi P, et al. Inhibition of glutathione S-transferase by ethacrynic acid augments ischemia-reperfusion damage and apoptosis and attenuates the positive effect of ischemic postconditioning in a bilateral acute hindlimb ischemia rat model. J Vasc Res. 2015;52:53–61. - PubMed
-
- Liu L, Fujimoto M, Kawakita F, et al. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor treatment suppresses early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage in mice. Mol Neurobiol. 2016;53:4529–38. - PubMed
-
- Liu JK, Ying M, Zhang JY, et al. Thioridazine upregulates programmed cell death 4 to induce apoptosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. Anti-Cancer Drugs. 2018;29:1. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

