The role of smooth muscle cells in plaque stability: Therapeutic targeting potential
- PMID: 31254285
- PMCID: PMC6780045
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.14779
The role of smooth muscle cells in plaque stability: Therapeutic targeting potential
Abstract
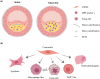
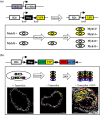
Events responsible for cardiovascular mortality and morbidity are predominantly caused by rupture of "vulnerable" atherosclerotic lesions. Vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) play a key role in atherogenesis and have historically been considered beneficial for plaque stability. VSMCs constitute the main cellular component of the protective fibrous cap within lesions and are responsible for synthesising strength-giving extracellular matrix components. However, lineage-tracing experiments in mouse models of atherosclerosis have shown that, in addition to the fibrous cap, VSMCs also give rise to many of the cell types found within the plaque core. In particular, VSMCs generate a substantial fraction of lipid-laden foam cells, and VSMC-derived cells expressing markers of macrophages, osteochondrocyte, and mesenchymal stem cells have been observed within lesions. Here, we review recent studies that have changed our perspective on VSMC function in atherosclerosis and discuss how VSMCs could be targeted to increase plaque stability.
© 2019 The British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ackers‐Johnson, M. , Talasila, A. , Sage, A. P. , Long, X. , Bot, I. , Morrell, N. W. , … Sinha, S. (2015). Myocardin regulates vascular smooth muscle cell inflammatory activation and disease. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 35(4), 817–828. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.305218 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aikawa, E. , Nahrendorf, M. , Figueiredo, J. L. , Swirski, F. K. , Shtatland, T. , Kohler, R. H. , … Weissleder, R. (2007). Osteogenesis associates with inflammation in early‐stage atherosclerosis evaluated by molecular imaging in vivo. Circulation, 116(24), 2841–2850. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.732867 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

