Pharmacokinetics of Risankizumab in Asian Healthy Subjects and Patients With Moderate to Severe Plaque Psoriasis, Generalized Pustular Psoriasis, and Erythrodermic Psoriasis
- PMID: 31257614
- PMCID: PMC6852105
- DOI: 10.1002/jcph.1473
Pharmacokinetics of Risankizumab in Asian Healthy Subjects and Patients With Moderate to Severe Plaque Psoriasis, Generalized Pustular Psoriasis, and Erythrodermic Psoriasis
Abstract
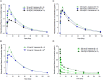
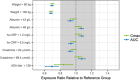
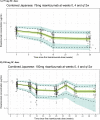
Risankizumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody that targets interleukin-23 p19 subunit, was developed for the treatment of psoriasis. This work characterizes risankizumab pharmacokinetics in Japanese and Chinese healthy subjects compared with white healthy subjects and in Japanese patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, generalized pustular psoriasis, or erythrodermic psoriasis. A phase 1, single-dose study evaluated risankizumab pharmacokinetics and safety/tolerability in healthy white (18 and 300 mg subcutaneous [SC]), Japanese (18, 90, and 300 mg SC and 200, 600, and 1200 mg intravenous [IV]), and Chinese (18, 90, and 300 mg SC) subjects; pharmacokinetic data were analyzed using noncompartmental methods. Risankizumab pharmacokinetic data from phase 2/3 studies in Japanese patients with plaque psoriasis, generalized pustular psoriasis, or erythrodermic psoriasis following multiple SC doses of 75 mg or 150 mg were analyzed using a population pharmacokinetic approach along with data from the phase 1 and global phase 1 to 3 studies. Risankizumab plasma exposures (peak plasma concentration and area under the concentration-time curve) were approximately dose-proportional across 18- to 300-mg SC or 200- to 1200-mg IV doses. Risankizumab terminal elimination half-life (harmonic mean 27-34 days) was comparable across doses and ethnicities. Risankizumab exposures were approximately 20% to 30% higher in Japanese and Chinese healthy subjects compared with white healthy subjects or in Japanese patients compared with non-Japanese patients. After accounting for body-weight differences, risankizumab exposures were comparable across ethnicities. Overall, there was no ethnic impact on risankizumab pharmacokinetics, and the small difference in exposure due to body weight has no clinical relevance.
Keywords: Japanese patients; erythrodermic psoriasis; ethnicity; generalized pustular psoriasis; plaque psoriasis; risankizumab.
© 2019 AbbVie Inc. The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American College of Clinical Pharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
Doerthe Eckert, Ahmed Suleiman, Yinuo Pang, Ling Cheng, and Ahmed A. Othman are employees of AbbVie and may hold AbbVie stock or stock options. Amit Khatri and Rajneet Oberoi are former employees of AbbVie and may hold AbbVie stock or stock options.
Figures
References
-
- Conrad C, Gilliet M. Psoriasis: from pathogenesis to targeted therapies. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018;54(1):102‐113. - PubMed
-
- Hoegler KM, John AM, Handler MZ, Schwartz RA. Generalized pustular psoriasis: a review and update on treatment. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32(10):1645‐1651. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

