The role of circular RNA HECTD1 expression in disease risk, disease severity, inflammation, and recurrence of acute ischemic stroke
- PMID: 31257675
- PMCID: PMC6757178
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.22954
The role of circular RNA HECTD1 expression in disease risk, disease severity, inflammation, and recurrence of acute ischemic stroke
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to explore the correlation of circular RNA HECT domain E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 (circRNA HECTD1) expression with disease risk, disease severity, inflammation, and recurrence of acute ischemic stroke (AIS).
Methods: A total of 160 initial AIS patients and 160 controls were enrolled in this study. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells of AIS patients and controls were separated from blood samples to detect circRNA HECTD1 expression by RT-qPCR. Inflammatory cytokines in serum of AIS patients were measured by ELISA. Furthermore, the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score was used to evaluate disease severity of AIS patients. Additionally, disease recurrence was documented during follow-up, and recurrence-free survival (RFS) was calculated.
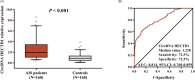
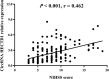
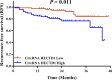
Results: CircRNA HECTD1 expression was higher in AIS patients than that in controls, and the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve revealed that circRNA HECTD1 expression was of a good value in distinguishing AIS patients from controls with area under the curve (AUC) of 0.814 (95% CI: 0.768-0.859). In AIS patients, circRNA HECTD1 expression was positively correlated with NIHSS score, CRP, and pro-inflammatory cytokines. CircRNA HECTD1 expression was increased in AIS recurrence patients compared to non-recurrence patients, and further, ROC curve analysis disclosed that circRNA HECTD1 expression predicted higher risk of AIS recurrence (AUC: 0.694, 95% CI: 0.586-0.801). Additionally, circRNA HECTD1 expression was negatively correlated with RFS.
Conclusions: CircRNA HECTD1 expression correlates with higher disease risk, disease severity, inflammation, and recurrence of AIS.
Keywords: acute ischemic stroke; circRNA HECTD1; inflammation; recurrence; severity.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 correlates with higher disease risk, worse disease condition, decreased miR-124 and miR-125a and predicts poor recurrence-free survival of acute ischemic stroke.J Clin Lab Anal. 2020 Feb;34(2):e23056. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23056. Epub 2019 Nov 12. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020. PMID: 31721299 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating long noncoding RNA ANRIL downregulation correlates with increased risk, higher disease severity and elevated pro-inflammatory cytokines in patients with acute ischemic stroke.J Clin Lab Anal. 2019 Jan;33(1):e22629. doi: 10.1002/jcla.22629. Epub 2018 Aug 1. J Clin Lab Anal. 2019. PMID: 30069916 Free PMC article.
-
The correlation of long non-coding RNA intersectin 1-2 with disease risk, disease severity, inflammation, and prognosis of acute ischemic stroke.J Clin Lab Anal. 2020 Feb;34(2):e23053. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23053. Epub 2019 Oct 24. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020. PMID: 31647141 Free PMC article.
-
CircRNA: A new target for ischemic stroke.Gene. 2025 Jan 15;933:148941. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2024.148941. Epub 2024 Sep 11. Gene. 2025. PMID: 39270759 Review.
-
The Role of Circular RNAs in Ischemic Stroke.Neurochem Res. 2023 Sep;48(9):2607-2620. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-03935-7. Epub 2023 May 1. Neurochem Res. 2023. PMID: 37126193 Review.
Cited by
-
Circular RNA expression profile in blood according to ischemic stroke etiology.Cell Biosci. 2020 Mar 10;10:34. doi: 10.1186/s13578-020-00394-3. eCollection 2020. Cell Biosci. 2020. PMID: 32175077 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding RNAs in acute ischemic stroke: from brain to periphery.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Jan 1;20(1):116-129. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-23-01292. Epub 2024 Mar 1. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 38767481 Free PMC article.
-
circHECTD1 attenuates apoptosis of alveolar epithelial cells in acute lung injury.Lab Invest. 2022 Sep;102(9):945-956. doi: 10.1038/s41374-022-00781-z. Epub 2022 Apr 19. Lab Invest. 2022. PMID: 35440759
-
A systematic review of the research progress of non-coding RNA in neuroinflammation and immune regulation in cerebral infarction/ischemia-reperfusion injury.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 7;13:930171. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.930171. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36275741 Free PMC article.
-
The functions of fluoxetine and identification of fluoxetine-mediated circular RNAs and messenger RNAs in cerebral ischemic stroke.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):2364-2376. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1935403. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34098829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Holmes DR Jr, Hopkins LN. Interventional cardiology and acute stroke care going forward: JACC review topic of the week. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73(12):1483‐1490. - PubMed
-
- Zerna C, Thomalla G, Campbell B, Rha JH, Hill MD. Current practice and future directions in the diagnosis and acute treatment of ischaemic stroke. Lancet. 2018;392(10154):1247‐1256. - PubMed
-
- Prabhakaran S, Ruff I, Bernstein RA. Acute stroke intervention: a systematic review. JAMA. 2015;313(14):1451‐1462. - PubMed
-
- Zerna C, Hegedus J, Hill MD. Evolving treatments for acute ischemic stroke. Circ Res. 2016;118(9):1425‐1442. - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Schuman E. Circular RNAs in brain and other tissues: a functional enigma. Trends Neurosci. 2016;39(9):597‐604. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

