Safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamic activity of obinutuzumab, a type 2 anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody for the desensitization of candidates for renal transplant
- PMID: 31257724
- PMCID: PMC6899639
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.15514
Safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamic activity of obinutuzumab, a type 2 anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody for the desensitization of candidates for renal transplant
Abstract
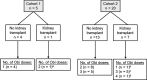
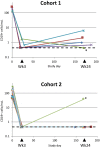
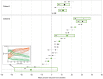
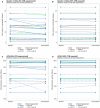
The limited effectiveness of rituximab plus intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) in desensitization may be due to incomplete B cell depletion. Obinutuzumab is a type 2 anti-CD20 antibody that induces increased B cell depletion relative to rituximab and may therefore be more effective for desensitization. This open-label phase 1b study assessed the safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of obinutuzumab in highly sensitized patients with end-stage renal disease. Patients received 1 (day 1, n = 5) or 2 (days 1 and 15; n = 20) infusions of 1000-mg obinutuzumab followed by 2 doses of IVIG on days 22 and 43. Eleven patients received additional obinutuzumab doses at the time of transplant and/or at week 24. The median follow-up duration was 9.4 months. Obinutuzumab was well tolerated, and most adverse events were grade 1-2 in severity. There were 11 serious adverse events (SAEs) in 9 patients (36%); 10 of these SAEs were infections and 4 occurred after kidney transplant. Obinutuzumab plus IVIG resulted in profound peripheral B cell depletion and appeared to reduce B cells in retroperitoneal lymph nodes. Reductions in anti-HLA antibodies, number of unacceptable antigens, and the calculated panel reactive antibody score as centrally assessed using single-antigen bead assay were limited and not clinically meaningful for most patients (NCT02586051).
Keywords: B cell biology; alloantibody; clinical research/practice; clinical trial; immunosuppressant - fusion proteins and monoclonal antibodies: B cell specific; immunosuppression/immune modulation; kidney transplantation/nephrology; pharmacology.
© 2019 The Authors. American Journal of Transplantation published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Figures

References
-
- Terasaki PI, Ozawa M. Predicting kidney graft failure by HLA antibodies: a prospective trial. Am J Transplant. 2004;4(3):438‐443. - PubMed
-
- Jordan SC, Pescovitz MD. Presensitization: the problem and its management. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;1(3):421‐432. - PubMed
-
- Meier‐Kriesche HU, Port FK, Ojo AO, et al. Effect of waiting time on renal transplant outcome. Kidney Int. 2000;58(3):1311‐1317. - PubMed
-
- Nankivell BJ, Alexander SI. Rejection of the kidney allograft. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(15):1451‐1462. - PubMed

