Identification and validation of microRNAs that synergize with miR-34a - a basis for combinatorial microRNA therapeutics
- PMID: 31258013
- PMCID: PMC6649554
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1634956
Identification and validation of microRNAs that synergize with miR-34a - a basis for combinatorial microRNA therapeutics
Abstract
Efforts to search for better treatment options for cancer have been a priority, and due to these efforts, new alternative therapies have emerged. For instance, clinically relevant tumor-suppressive microRNAs that target key oncogenic drivers have been identified as potential anti-cancer therapeutics. MicroRNAs are small non-coding RNAs that negatively regulate gene expression at the posttranscriptional level. Aberrant microRNA expression, through misexpression of microRNA target genes, can have profound cellular effects leading to a variety of diseases, including cancer. While altered microRNA expression contributes to a cancerous state, restoration of microRNA expression has therapeutic benefits. For example, ectopic expression of microRNA-34a (miR-34a), a tumor suppressor gene that is a direct transcriptional target of p53 and thus is reduced in p53 mutant tumors, has clear effects on cell proliferation and survival in murine models of cancer. MicroRNA replacement therapies have recently been tested in combination with other agents, including other microRNAs, to simultaneously target multiple pathways to improve the therapeutic response. Thus, we reasoned that other microRNA combinations could collaborate to further improve treatment. To test this hypothesis miR-34a was used in an unbiased cell-based approach to identify combinatorial microRNA pairs with enhanced efficacy over miR-34a alone. This approach identified a subset of microRNAs that was able to enhance the miR-34a antiproliferative activity. These microRNA combinatorial therapeutics could offer superior tumor-suppressive abilities to suppress oncogenic properties compared to a monotherapeutic approach. Collectively these studies aim to address an unmet need of identifying, characterizing, and therapeutically targeting microRNAs for the treatment of cancer.
Keywords: Mirna-34; combinatorial therapeutics; miR-34; miR-34a; miRNA therapeutics; synergism.
Figures
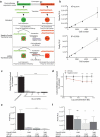
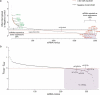
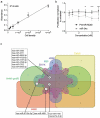
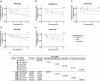
References
-
- Wightman B, Ha I, Ruvkun G.. Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell. 1993;75:855–862. - PubMed
-
- Reinhart BJ, Slack FJ, Basson M, et al. The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 2000;403:901–906. - PubMed
-
- Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75:843–854. - PubMed
-
- Hermeking H. The miR-34 family in cancer and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2010;17:193–199. - PubMed
-
- Gallardo E, Navarro A, Viñolas N, et al. miR-34a as a prognostic marker of relapse in surgically resected non-small-cell lung cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30:1903–1909. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
